Countries in Eastern Europe and Their Capitals
Eastern European countries are grouped according to their cultural and historical characteristics. On one hand, they bring together countries that came under the influence of the Orthodox Church and have the Slavic language. Many of them like Serbia, Montenegro, Croatia were dominated by the Turkish-Ottoman Empire. That is why we find a large number of Muslims established there several centuries ago.
On the other hand, regions such as Hungary, the Czech Republic and Slovakia were part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. They have a culture close to the west, although they were not occupied by the Roman Empire.
How Many Countries in Eastern Europe
As a region of Europe, Eastern Europe is composed of 10 independent countries (Belarus, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Hungary, Moldova, Poland, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Ukraine). See below for the list of East European countries and dependencies by population. Also, you can find all of them in alphabetical order at this end of this page.
1. Belarus
Belarus, formally the Republic of Belarus, is a country in Eastern Europe. The country is an inland state and borders Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia and Ukraine.
 |
|
2. Bulgaria
Bulgaria is a republic in southern Europe in the northeastern Balkans, bordering Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west and Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea coast to the east. Bulgaria has about 7.2 million residents and Sofia is the capital and largest city.
 |
|
3. Czech republic
The Czech Republic, formally the Czech Republic, is a Central European country and a member of the European Union.
 |
|
4. Hungary
Hungary is a republic in Central Europe. The capital of Hungary is Budapest. The country borders Austria, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia and Slovenia. Hungary dates back to the ninth century and the population speaks the Ugric language Hungarian.
 |
|
5. Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a republic in Eastern Europe bordering Romania and Ukraine. The country has a population of 3.5 million.
 |
|
6. Poland
Poland, formally the Republic of Poland, is a republic in Central Europe. Poland borders Germany to the west, the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south, Ukraine and Belarus to the east, and Lithuania and Russia to the north.
 |
|
7. Romania
Romania is a republic in Eastern Europe. The country is bordered to the north by Ukraine, to the east by Moldova and the Black Sea, to the south by Bulgaria, along the river Danube, and to the west by Hungary and Serbia.
 |
|
8. Russia
Russia, formally the Russian Federation, is a federal republic that encompasses large parts of Eastern Europe and all of North Asia.
 |
|
9. Slovakia
Slovakia is a republic in Central Europe bordering Poland, Ukraine, Hungary, Austria and the Czech Republic.
 |
|
10. Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It borders Romania, Moldova, Hungary, Slovakia, Poland, Belarus and Russia. To the south, the country has a coast facing the Black Sea.
 |
|
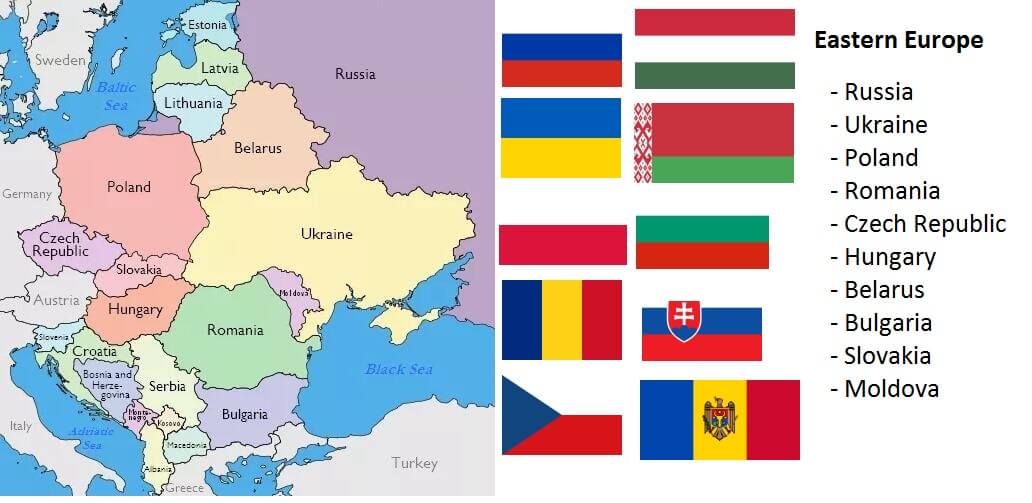
List of Countries in Eastern Europe and Their Capitals
As noted above, there are 3 independent countries in the Eastern Europe. Among them, the largest country is Russia and the smallest is Moldova. The full list of Eastern European countries with capitals is shown in the table below, ranked by latest total population.
| Rank | Independent Country | Current Population | Capital |
| 1 | Russia | 146,793,744 | Moscow |
| 2 | Ukraine | 42,079,547 | Kiev |
| 3 | Poland | 38,413,000 | Warsaw |
| 4 | Romania | 19,523,621 | Bucharest |
| 5 | Czech Republic | 10,652,812 | Prague |
| 6 | Hungary | 9,764,000 | Budapest |
| 7 | Belarus | 9,465,300 | Minsk |
| 8 | Bulgaria | 7,000,039 | Sofia |
| 9 | Slovakia | 5,450,421 | Bratislava |
| 10 | Moldova | 3,547,539 | Chisinau |
Map of Countries in Eastern Europe
Brief History of Eastern Europe
Ancient and Early Medieval Period
Early Civilizations and Tribal Societies
Eastern Europe, encompassing regions such as the Balkans, the Baltic states, and Eastern Slavic lands, has a diverse and complex history. Early inhabitants included Thracians, Illyrians, and Dacians in the Balkans, and Baltic tribes in the north. The Scythians and Sarmatians roamed the steppes, while Slavic tribes began to settle in the region around the 5th century CE, forming the foundations of future states.
Byzantine Influence and Slavic Expansion
The Byzantine Empire significantly influenced the Balkans, spreading Christianity, art, and architecture. The Eastern Orthodox Church played a vital role in shaping the cultural and religious identity of Eastern Europe. Slavic tribes, including the ancestors of modern Russians, Ukrainians, and Belarusians, expanded into Eastern Europe, integrating with local populations and establishing early polities.
High Medieval Period
Kievan Rus’ and the Rise of Principalities
The formation of Kievan Rus’ in the 9th century marked a significant development in Eastern European history. Founded by the Varangians, Kievan Rus’ became a powerful federation of Slavic tribes under the leadership of the Grand Prince of Kiev. The Christianization of Kievan Rus’ in 988 under Prince Vladimir the Great established Eastern Orthodoxy as the dominant religion.
The Mongol Invasion and the Golden Horde
In the 13th century, the Mongol invasion devastated Eastern Europe, leading to the subjugation of Kievan Rus’ by the Golden Horde. The Mongol yoke profoundly impacted the region, causing political fragmentation and economic hardship. However, some principalities, like Moscow, began to rise in power by collaborating with the Mongols and gradually asserting independence.
Late Medieval and Early Modern Period
The Rise of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
The 14th and 15th centuries saw the emergence of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, a powerful state formed through the Union of Krewo (1385) and the Union of Lublin (1569). The Commonwealth became one of the largest and most populous states in Europe, characterized by its unique system of “Golden Liberty,” which granted significant political rights to the nobility.
Ottoman Expansion and Habsburg Influence
The Ottoman Empire’s expansion into the Balkans in the 14th and 15th centuries significantly impacted Eastern Europe. The fall of Constantinople in 1453 marked the beginning of Ottoman dominance in Southeastern Europe, leading to centuries of Turkish influence in the region. Concurrently, the Habsburgs extended their control over parts of Eastern Europe, especially in Hungary and the western Balkans, contributing to the complex political landscape.
Modern Period
The Partitions of Poland and Rise of Russia
The late 18th century witnessed the partitions of Poland (1772, 1793, 1795) by Russia, Prussia, and Austria, leading to the disappearance of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth from the map. Meanwhile, the Russian Empire expanded its territory, becoming a dominant power in Eastern Europe. The rise of the Russian Empire under leaders like Peter the Great and Catherine the Great brought significant modernization efforts and territorial expansion.
Nationalism and Independence Movements
The 19th century was marked by the rise of nationalism and independence movements across Eastern Europe. The decline of the Ottoman Empire and the weakening of Habsburg control allowed for the emergence of new national states. The Greek War of Independence (1821-1830) inspired other Balkan nations to seek independence. The revolutions of 1848 also had a significant impact, fostering national consciousness and political change.
20th Century Turmoil
World War I and the Treaty of Versailles
World War I and the subsequent Treaty of Versailles (1919) dramatically reshaped Eastern Europe. The collapse of empires led to the creation of new states, including Poland, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia. The interwar period was marked by political instability, economic challenges, and the rise of authoritarian regimes.
World War II and Soviet Domination
World War II brought devastation to Eastern Europe, with significant battles and atrocities occurring in the region. The Nazi occupation and the Holocaust had a profound impact on Eastern European populations. After the war, the Soviet Union established control over Eastern Europe, leading to the formation of communist governments aligned with Moscow. The Iron Curtain divided Europe, creating a geopolitical and ideological divide that lasted until the end of the Cold War.
Contemporary Developments
The Fall of Communism and Democratic Transitions
The late 20th century saw the collapse of communist regimes across Eastern Europe, starting with the Solidarity movement in Poland and culminating in the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989. The subsequent dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 allowed for the independence of Baltic states and other Eastern European nations. These countries embarked on paths toward democracy, market economies, and integration with Western institutions.
European Union Integration and Modern Challenges
In the 21st century, many Eastern European countries joined the European Union and NATO, seeking stability, security, and economic growth. However, the region faces ongoing challenges, including political corruption, economic disparities, and tensions with Russia. Conflicts like the war in Ukraine underscore the continuing geopolitical volatility in Eastern Europe.













































