Uganda Population
Uganda is rich in natural resources, but has suffered from poor leaders and many internal unrest. The country is still struggling with poverty and inequality.
Key figures and facts
- Capital: Kampala
- Ethnic groups: Baganda 16.5%, Banyakole 9.6%, Basoga 8.8%, Bakiga 7.1%, Iteso 7%, Langi 6.3%, Bagisu 4.9%, Acholi 4.4%, Lugbara 3.3%, others 32.1% (2014)
- Language: English, Ganda/Luganda, Niger-Congo, Nilo-Saharan, Swahili, Arabic
- Religion: Protestants 45.1%, Roman Catholic 39.3%, Muslims 13.7%, others 1.6%, none 0.2% (2014)
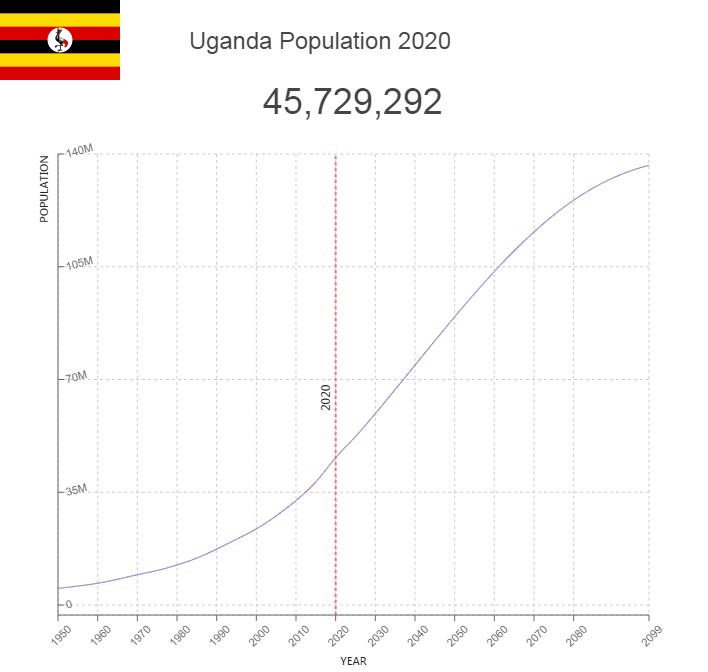
- Population: 44 495 000 (2018)
- Control Form: Republic
- Area: 241 038 km2
- Currency: Ugandan shilling
- GNP per capita: 1 819 PPP $
- National Day: October 9th
Uganda’s Population
Uganda has a population of 43 252 000 (2020). Most of the population lives in rural areas. Population density averages 215 residents per square kilometer (2017). Population density is highest in areas where the soil is most fertile, such as the area opposite the northern shores of Lake Victoria, between Kampala and Jinja.
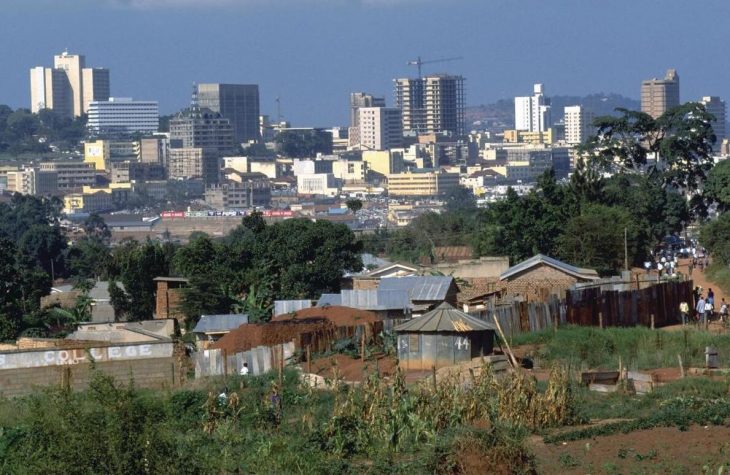

Population of Uganda by Year (Historical)
| Year | Population | Annual Growth Rate | Population Density | Global Rank |
| 2020 | 45,740,896 | 3.320% | 228.9225 | 31 |
| 2019 | 44,269,483 | 3.600% | 221.5584 | 32 |
| 2018 | 42,728,925 | 3.790% | 213.8483 | 33 |
| 2017 | 41,166,477 | 3.830% | 206.0287 | 34 |
| 2016 | 39,649,055 | 3.720% | 198.4343 | 35 |
| 2015 | 38,225,342 | 3.340% | 191.3090 | 35 |
| 2010 | 32,428,056 | 3.210% | 162.2950 | 37 |
| 2005 | 27,684,474 | 3.200% | 138.5546 | 39 |
| 2000 | 23,650,061 | 2.990% | 118.3633 | 42 |
| 1995 | 20,413,041 | 3.300% | 102.1628 | 46 |
| 1990 | 17,354,281 | 3.570% | 86.8545 | 47 |
| 1985 | 14,559,244 | 3.190% | 72.8660 | 50 |
| 1980 | 12,442,223 | 2.990% | 62.2708 | 52 |
| 1975 | 10,737,292 | 2.680% | 53.7381 | 52 |
| 1970 | 9,405,489 | 3.330% | 47.0727 | 56 |
| 1965 | 7,985,955 | 3.370% | 39.9683 | 61 |
| 1960 | 6,766,984 | 2.820% | 33.8676 | 65 |
| 1955 | 5,888,682 | 2.680% | 29.4720 | 65 |
| 1950 | 5,158,079 | 0.000% | 25.8155 | 65 |
Major Cities in Uganda by Population
| Rank | City | Population |
| 1 | Kampala | 1,353,078 |
| 2 | Gulu | 146,747 |
| 3 | Lira | 119,212 |
| 4 | Mbarara | 97,389 |
| 5 | Jinja | 92,950 |
| 6 | Bwizibwera | 79,046 |
| 7 | Mbale | 76,382 |
| 8 | Mukono | 67,179 |
| 9 | Kasese | 67,158 |
| 10 | Masaka | 65,262 |
| 11 | Entebbe | 62,858 |
| 12 | Njeru | 61,841 |
| 13 | Kitgum | 56,780 |
| 14 | Soroti | 56,289 |
| 15 | Arua | 55,474 |
| 16 | Iganga | 44,913 |
| 17 | Kabale | 43,389 |
| 18 | Busia | 43,089 |
| 19 | Fort Portal | 42,559 |
| 20 | Mityana | 41,020 |
| 21 | Tororo | 40,289 |
| 22 | Hoima | 39,514 |
| 23 | Lugazi | 34,925 |
| 24 | Masindi | 31,375 |
| 25 | Ibanda | 30,889 |
| 26 | Pallisa | 30,634 |
| 27 | Nyachera | 30,398 |
| 28 | Nebbi | 30,243 |
| 29 | Adjumani | 28,589 |
| 30 | Paidha | 28,237 |
| 31 | Luwero | 28,227 |
| 32 | Wobulenzi | 24,304 |
| 33 | Yumbe | 24,189 |
| 34 | Namasuba | 22,396 |
| 35 | Bugiri | 22,389 |
| 36 | Kayunga | 21,593 |
| 37 | Wakiso | 20,419 |
| 38 | Mubende | 18,825 |
| 39 | Kotido | 18,689 |
| 40 | Moyo | 18,689 |
| 41 | Kyenjojo | 18,489 |
| 42 | Kireka | 17,836 |
| 43 | Kamwenge | 17,058 |
| 44 | Bundibugyo | 16,808 |
| 45 | Ntungamo | 16,804 |
| 46 | Busembatia | 15,778 |
| 47 | Ntungamo | 15,189 |
| 48 | Buwenge | 15,019 |
| 49 | Kanungu | 14,489 |
| 50 | Kiboga | 14,401 |
| 51 | Kiruhura | 13,889 |
| 52 | Rukungiri | 13,889 |
| 53 | Sironko | 13,889 |
| 54 | Kamuli | 12,653 |
| 55 | Kisoro | 12,289 |
| 56 | Apac | 11,665 |
| 57 | Pader | 11,489 |
| 58 | Bugembe | 11,487 |
| 59 | Mayuge | 11,392 |
| 60 | Bweyogerere | 11,362 |
| 61 | Kumi | 11,289 |
| 62 | Kapchorwa | 11,189 |
| 63 | Pader Palwo | 11,041 |
| 64 | Mpigi | 10,971 |
| 65 | Moroto | 10,189 |
| 66 | Kyotera | 8,361 |
| 67 | Lyantonde | 7,928 |
| 68 | Kilembe | 7,803 |
| 69 | Masindi Port | 7,717 |
| 70 | Byakabanda | 7,497 |
| 71 | Kajansi | 7,419 |
| 72 | Nakasongola | 6,810 |
| 73 | Kigorobya | 5,309 |
| 74 | Kibale | 5,089 |
| 75 | Margherita | 4,998 |
Population Composition
Key figures describing population composition and social conditions:
- 2 percent of the population is aged 0-14 (2020).
- 25 percent of the population lives in cities (2020).
- The average life expectancy is 70.5 years for women and 66 years for men (2020).
- Each woman has an average of 5.5 children (2020).
- The infant mortality rate is 32.6 per 1000 live births (2020).
- HIV and AIDS: 5.7 percent of the population (1.4 million) live with HIV/AIDS (2018). Each year, there are around 150,000 new infected.
- Uganda is categorized as a LDC, least developed country, by the UN. 41.7 percent of the population lives in extreme poverty (2017).
Ethnicity
There are around forty different population groups in Uganda. These tend to be divided into four main groups based on language groups: West Nilotic groups, East Nilotic groups, Bantu groups and groups that speak Sudanese languages.
The largest population group is baganda, which is believed to constitute around 16.5 percent of the population (2014). These live mainly in the central part of Uganda. Baganda belongs to the bantu groups, and other big bantu groups in Uganda are banyan school, basoga and bakiga. East of the country, the iteso group, which is the largest east nilotic group, belongs. Langi and acholi are the dominant groups in the north, these belong to western nilotic groups.
In the mountain area west of Uganda, there have traditionally been people belonging to the batwa group, formerly called pygmies. These have been largely displaced from their traditional areas due to rain forest destruction, and are now a vulnerable group socially.
Refugees and internally displaced persons
Uganda has at times housed large groups of refugees from countries in the region. The largest refugee groups from DR Congo, Somalia and Sudan. There are currently around 225,000 refugees in Uganda (UNHCR 2013).
Religion
The majority in Uganda are Christians, of whom 45 percent are Protestants and 39 percent Catholics (2014). In recent years, free church churches have gained greater support. American Free Churches have played a role in the development of stricter condemnation of homosexuality in Uganda.
About 13 percent of the population are Muslims, most of whom live in northern Uganda. In addition, it is believed that one-tenth of the population practices traditional religions. Many people blend Christianity or Islam with elements of traditional religion.
Language
English is the official language and teaching language, in addition there are around forty different local languages spoken. These are divided into four language groups: Western Nilotic languages, Eastern Nilotic languages, Bantu languages and Sudanese languages.
Uganda, a bantu language, is the most widely used, and Uganda is also used as a commercial language in large parts of the country. Swahili is less used in Uganda than in neighboring Tanzania and Kenya, this is mainly because Swahili is linked to the military in Uganda.













































