Venezuela Population
Venezuela has the world’s largest oil reserves, and the country is entirely dependent on oil revenues. The money was spent on social programs under President Hugo Chávez (1999-2013), until the oil price plunged in 2014. Now the country is in a humanitarian crisis, under an increasingly authoritarian and corrupt regime.
Key figures and facts
- Capital: Caracas
- Ethnic groups: Spaniards, Italians, Portuguese, Arabs, Germans, Africans and various foreigners.
- Language: Spanish, various minor tribal languages
- Religion: Catholics 96%, Protestant Christians 2%, other 2%
- Population: 32 381 221 (2018)
- Control Form: Federal Republic
- Area: 912 050 km2
- Currency: Bolivar
- National Day: July 5th
Venezuela Population
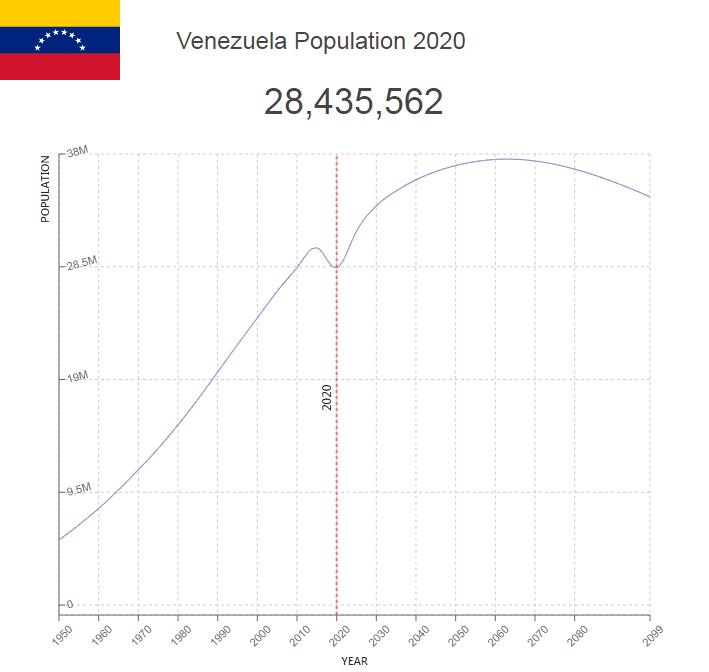
Venezuela has just over 31,600,000 residents (2018), and annual population growth is 1.2 percent. The median age is 28.7 years, and life expectancy at birth is 79.3 years for women and 73.2 years for men. The fertility rate is 2.3 children per woman.

The escalating economic crisis since 2014 has led to a humanitarian crisis in the form of hunger, drug shortages and migration out of the country. By the end of 2018, the number of Venezuelans abroad was estimated to be three million, compared to just under 700,000 in 2015.
Population of Venezuela by Year (Historical)
| Year | Population | Annual Growth Rate | Population Density | Global Rank |
| 2020 | 28,435,829 | -0.280% | 32.2385 | 50 |
| 2019 | 28,515,718 | -1.290% | 32.3290 | 50 |
| 2018 | 28,887,007 | -1.750% | 32.7500 | 48 |
| 2017 | 29,402,373 | -1.500% | 33.3343 | 46 |
| 2016 | 29,851,144 | -0.770% | 33.8430 | 45 |
| 2015 | 30,081,718 | 1.130% | 34.1044 | 45 |
| 2010 | 28,439,829 | 1.470% | 32.2430 | 43 |
| 2005 | 26,432,336 | 1.790% | 29.9671 | 41 |
| 2000 | 24,192,335 | 1.980% | 27.4275 | 40 |
| 1995 | 21,930,973 | 2.240% | 24.8638 | 41 |
| 1990 | 19,632,554 | 2.540% | 22.2580 | 43 |
| 1985 | 17,319,409 | 2.670% | 19.6355 | 42 |
| 1980 | 15,182,500 | 2.850% | 17.2129 | 42 |
| 1975 | 13,189,398 | 2.970% | 14.9532 | 47 |
| 1970 | 11,396,282 | 3.290% | 12.9203 | 46 |
| 1965 | 9,692,167 | 3.550% | 10.9884 | 49 |
| 1960 | 8,141,730 | 3.840% | 9.2306 | 53 |
| 1955 | 6,744,584 | 4.230% | 7.6466 | 60 |
| 1950 | 5,481,867 | 0.000% | 6.2150 | 64 |
Major Cities in Venezuela by Population
| Rank | City | Population |
| 1 | Caracas | 2,999,889 |
| 2 | Maracaibo | 2,224,889 |
| 3 | Maracay | 1,754,145 |
| 4 | Valencia | 1,384,972 |
| 5 | Barquisimeto | 809,379 |
| 6 | Ciudad Guayana | 746,424 |
| 7 | Barcelona | 424,684 |
| 8 | Maturin | 410,861 |
| 9 | Puerto La Cruz | 369,889 |
| 10 | Petare | 364,573 |
| 11 | Barinas | 353,331 |
| 12 | Turmero | 344,589 |
| 13 | Ciudad Bolivar | 337,889 |
| 14 | Merida | 299,889 |
| 15 | Alto Barinas | 284,178 |
| 16 | Santa Teresa del Tuy | 278,779 |
| 17 | Cumana | 257,672 |
| 18 | San Cristobal | 246,472 |
| 19 | Nuestra Senora del Rosario de Baruta | 244,105 |
| 20 | Mucumpiz | 215,148 |
| 21 | Cabimas | 200,707 |
| 22 | Coro | 195,116 |
| 23 | Guatire | 191,792 |
| 24 | Cua | 182,447 |
| 25 | Guarenas | 181,501 |
| 26 | Puerto Cabello | 173,889 |
| 27 | Ocumare del Tuy | 165,961 |
| 28 | Guacara | 151,641 |
| 29 | El Tigre | 150,888 |
| 30 | El Limon | 148,136 |
| 31 | Acarigua | 143,593 |
| 32 | Los Teques | 140,506 |
| 33 | Punto Fijo | 131,673 |
| 34 | Charallave | 129,071 |
| 35 | Palo Negro | 128,764 |
| 36 | Cagua | 118,922 |
| 37 | Anaco | 117,485 |
| 38 | Calabozo | 117,021 |
| 39 | Guanare | 112,175 |
| 40 | Carupano | 111,971 |
| 41 | Ejido | 106,804 |
| 42 | Catia La Mar | 106,711 |
| 43 | Mariara | 105,375 |
| 44 | Carora | 93,677 |
| 45 | Valera | 93,645 |
| 46 | Yaritagua | 89,551 |
| 47 | Valle de La Pascua | 88,969 |
| 48 | San Juan de los Morros | 87,628 |
| 49 | Porlamar | 87,009 |
| 50 | La Victoria | 86,934 |
| 51 | Tinaquillo | 82,034 |
| 52 | El Cafetal | 79,918 |
| 53 | San Fernando de Apure | 78,668 |
| 54 | San Carlos | 77,081 |
| 55 | San Felipe | 76,655 |
| 56 | Villa de Cura | 76,503 |
| 57 | Araure | 72,943 |
| 58 | Guigue | 71,419 |
| 59 | La Villa del Rosario | 64,900 |
| 60 | Chacao | 64,498 |
| 61 | San Antonio de Los Altos | 63,762 |
| 62 | Machiques | 62,857 |
| 63 | San Jose de Guanipa | 62,017 |
| 64 | El Vigia | 58,981 |
| 65 | Caucaguita | 58,889 |
| 66 | Punta Cardon | 58,815 |
| 67 | Los Dos Caminos | 58,057 |
| 68 | El Hatillo | 57,480 |
| 69 | La Dolorita | 56,735 |
| 70 | San Carlos del Zulia | 56,471 |
| 71 | Upata | 53,574 |
| 72 | El Tocuyo | 52,988 |
| 73 | Maiquetia | 52,453 |
| 74 | Caucaguito | 52,445 |
| 75 | Puerto Ayacucho | 52,415 |
| 76 | Rubio | 51,457 |
| 77 | Tucupita | 51,423 |
| 78 | San Mateo | 50,290 |
| 79 | Chivacoa | 45,793 |
| 80 | Moron | 44,197 |
| 81 | Lagunillas | 44,146 |
| 82 | San Joaquin | 41,519 |
| 83 | Quibor | 41,415 |
| 84 | Zaraza | 41,372 |
| 85 | Carrizal | 40,507 |
| 86 | Altagracia de Orituco | 39,941 |
| 87 | Gueiria | 39,889 |
| 88 | Tacarigua | 39,094 |
| 89 | Colon | 38,122 |
| 90 | Trujillo | 37,999 |
| 91 | Caraballeda | 37,713 |
| 92 | La Asuncion | 34,973 |
| 93 | Los Rastrojos | 34,525 |
| 94 | Barinitas | 34,286 |
| 95 | Las Tejerias | 33,209 |
| 96 | Cantaura | 32,929 |
| 97 | San Antonio del Tachira | 32,347 |
| 98 | Santa Rita | 31,699 |
| 99 | Guasdualito | 30,749 |
| 100 | Nirgua | 30,077 |
| 101 | Santa Elena de Uairen | 29,684 |
| 102 | Juan Griego | 28,145 |
| 103 | Villa Bruzual | 27,882 |
| 104 | Tariba | 27,321 |
| 105 | La Fria | 26,966 |
| 106 | La Guaira | 25,148 |
| 107 | Chichiriviche | 12,389 |
| 108 | Tucacas | 12,389 |
Demographic composition
In pre-Columbian times, the people of present-day Venezuela consisted of a number of Caribbean- and Arawak- speaking indigenous groups. Possibly as many as one million people lived on what is now Venezuelan territory when colonialization began in the 16th century. The indigenous population was greatly reduced after a short time due to massacres, illness and slavery.
Immigration in several different phases throughout history, as well as the introduction of slaves from Africa, has created a population composed of Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Arabic, German, African and indigenous people. The country also has a large immigrant group from other Latin American countries, especially neighboring Colombia.
In a 2011 census, 51.6 percent of the population identified themselves as mastis (mixed origin), 43.6 percent as white, 2.9 percent as black, 0.7 of African origin, and 1.2 percent as “other”.
About two percent of the population belongs to indigenous groups, the highest proportion of indigenous people found in the states of Amazonas and Zulia. There are estimated to be at least 26 different indigenous groups in the country; among the largest are guajiro, warao, piaroa, yanomamo and bari (motilon).
Demographic distribution
Venezuela has traditionally had a very high population growth. Only during the 1970s and 1980s did the growth rate begin to decline.
The average population density is 33.74 people per square kilometer, but the country is unevenly inhabited; the areas south and east of Orinoco have only about four percent of the population, while the coastal and valley areas in the north are densely populated.
Growth in the oil economy in the years following the Second World War led to a significant migration from the countryside to the cities, with around 88 percent of the population now living in cities, with an annual urbanization rate of 1.3 percent. The largest cities (2018) are the capital Caracas (2 935 million residents), Maracaibo (2 179 million residents) and Valencia (1 734 million residents).
Health and welfare
Living standards increased and poverty dropped significantly from 2004 to 2012 as a result of economic boom and a comprehensive expansion of the education system, health care and other welfare services. However, since 2014, the population has undergone a dramatic fall in living standards as a result of a major economic crisis. This has also led to an increase in key indicators such as infant mortality, maternal mortality, and child malnutrition. However, there are few official figures available in recent years.
The government has not published poverty statistics since 2015, but a survey conducted by the country’s largest private universities estimates the income-based poverty rate in 2017 to be 87 percent.
97 percent of the population is estimated to be able to read and write (2016), and the average length of schooling is 9.4 years (2014).
Migration Crisis
Venezuela had a net migration rate of -1.2 in 2017. According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNCHR), by the end of 2018, there were three million migrants and refugees from Venezuela worldwide. 2.4 million of these are in neighboring countries in South America and the Caribbean, while the most resourceful migrants are moving to the US and Europe.
The largest receiving country is Colombia with one million migrants, and many cross the border between Venezuela and Colombia on foot. Furthermore, Peru, Ecuador, Argentina, Chile and Brazil are the largest receiving countries. There have been several reports of Venezuelans being exposed to racism, exploitation, discrimination and harassment in the countries they are migrating to.
The reasons why Venezuelans leave the country are complex, including unemployment, crime, lack of purchasing power to meet basic needs including food and medicine, lack of access to social services and fear of political persecution. Since 2014, there has been a 2000 percent increase in asylum applications provided by Venezuelans worldwide; in 2017, the figure was a total of 94,284 applications.
Religion
Venezuela has freedom of religion. In a 2011 census, 71 percent stated that they were Catholics, 17 percent that they were Protestants, eight percent that they were agnostics/atheists, and three percent “other religions.” In the latter category you also find syncretic forms of belief such as santería. Charismatic Protestant movements are widespread.
Language
The official language is Spanish. Most local indigenous languages belong to the carib, arawak and chibcha language groups.













































