Where is Venezuela Located?
Where is Venezuela located on the map? Venezuela is an independent nation located in South America. Check out the following images to see location of Venezuela on maps.
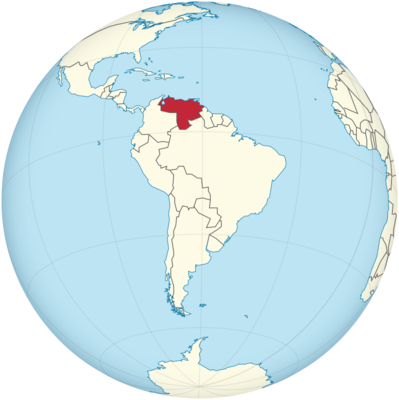
Venezuela Location in World Map
Venezuela is located in South America, in the northwest of the continent. It borders the Atlantic coast, which is a proud 2800 kilometers long. Most of it belongs to the Caribbean Sea. Venezuela has national borders with Colombia in the west and Guyana and Brazil in the east and south. The outline of the country is somewhat reminiscent of a triangle.
The equator runs just south of Venezuela. Venezuela can be divided into four major natural areas: the Andes, the Orinoco plain, the Maracaibo lowlands and the Guyana highlands.
Venezuela is located in the northwest of South America.
Islands
Numerous islands in the Caribbean Sea belong to Venezuela. This also includes Isla Margarita and its small neighboring islands Coche and Cubagua. The island of Tortuga is also part of Venezuela. It is only occasionally inhabited by fishermen. Close to the coast are the island states of Trinidad and Tobago as well as Aruba and Grenada, but also the islands of Bonaire and Curaçao, which belong to the Netherlands.
Guiana Esequiba
A large area that belongs to the state of Guiana is still claimed by Venezuela today. In 1899 it was awarded to Great Britain in an arbitration award, and in 1963 Guiana became independent. Venezuela does not recognize this to this day.
The map shows you the political structure of the country. The red striped area is claimed by Venezuela, but it belongs to Guyana. Click on the map, then you can also see the islands. Margarita Island is the one in purple.
Mountains
The Andes
In the west of the country, the Andes come in an arc from Colombia. The Andes mountain range stretches across the entire west coast of South America and ends here in Venezuela. The Andes can in turn be divided into individual mountain ranges. In the west of Venezuela rises the Mérida Cordillera, the continuation of the great Eastern Cordillera of the Andes. Here is also the highest mountain in the country, the Pico Bolívar. It is 4981 meters high. Like some of the other surrounding peaks, it is covered in snow all year round.
A large part of Venezuela’s population lives in the valleys of the Andes. Big cities like Valencia, Barquisimeto or Mérida are located here. After a depression, another mountain range follows on the coast, the Central Cordillera ( Cordillera Central or Cordillera Caribe ). This can in turn be divided into the northern coastal cordillera and the southern Serranía del Interior. Even further east, separated by the Unare Depression, the mountains continue into the eastern Cordillera ( Cordillera Oriental ).
The Orinoco Plain or Llanos
The Orinoco Plain stretches across Colombia and Venezuela. In the west the Andes border the plain, in the north the coast and in the south the Orinoco river. There is mainly grassland here. On the coast, the Orinoco forms a wide, swampy delta. The word Llano is Spanish and means level. After that, this landscape is also called the Llanos.
Maracaibo lowlands
In western Venezuela, between the Central Cordillera and the Merida Cordillera, lies the Maracaibo Lowland. In its center is Lake Maracaibo. It is actually an inland sea, as it is connected to the Gulf of Venezuela by a 75-kilometer strait. The city, also called Maracaibo, is located on the western bank of this strait. It is the second largest city in the country.
The area northeast of the lowlands is sometimes viewed as a separate landscape. It is called Coriano and is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Venezuela. You can see it on the natural space map in pink.
The Gulf of Venezuela, in turn, is bounded by the Guajira Peninsula (which largely belongs to Colombia) and the Paraguaná Peninsula. The landscape here is very dry and desert-like. The land bridge to Paraguaná with its large dunes belongs to the Médanos National Park.
Guiana Highlands (Guiana Shield)
The Guiana Mountains extend southeast of the Orinoco. More than half of the country is one of them. On the border with the state of Guyana lies the Gran Sabana, a plateau with flat valleys from which the tepuis protrude. These are large table mountains that were created by erosion. With their steep walls, they rise up to 1000 meters above the rainforest. Some tepuis have never been entered by a human. There are long cave systems in the tepuis and the highest waterfalls in the world tumble down from them. The highest, free falling waterfall in the world is also here, the Salto Àngel. It falls 978 meters!
Rivers and Lakes
Venezuela is crossed by more than a thousand rivers. The Orinoco is Venezuela’s longest river at 2,574 kilometers. It rises near the Brazilian border in the Guyana highlands and then flows in a wide arc towards the Atlantic. The Orinoco is the second longest river in South America after the Amazon. The Río Caroní and Río Apure are important tributaries of the Orinoco.
Climate
Venezuela is in the tropics. Temperatures hardly fluctuate all year round. The temperature difference between day and night is greater than over the year. The temperatures themselves depend on the altitude of a place. In the mountains it gets cooler the higher you go.
It is particularly hot on the Caribbean coast and in the lowlands. The average annual temperature is 26 to 28 degrees. In the higher-lying capital Caracas this is 21 degrees. Most of the cities are in the Andean valleys with a temperate climate. From an altitude of 2000 meters, it gets significantly cooler at 9 degrees.
Seasons cannot be distinguished here, but rainy and dry seasons. Most of the country has the rainy season between May and October.
Venezuela Facts
| Size | 912,050 km² |
| Residents | 28.8 million |
| Languages | Spanish (official language) and 31 regional languages |
| Capital | Caracas |
| Longest river | Orinoco (2,140 km) |
| Highest mountain | Pico Bolívar (4,981 m) |
| Currency | Bolívar |