North Korea Population
North Korea is one of the world’s strictest dictatorships and most isolated societies. Today, the country’s relationship with the outside world is strained by repeated nuclear test blasts and rocket launches.
Key figures and facts
- Capital: Pyongyang
- Ethnic groups: Almost exclusively Koreans, a few Chinese and Japanese
- Language: Korean
- Religion: Buddhists, Confucianists, some Christian and minor religious groups (NB: Independent religious activity is virtually non-existent. The government sponsors some religious groups to make it look like there is religious freedom in the country)
- Population: 25 610 672
- Control Form: Communist dictatorship
- Area: 120 540 km2
- Currency: won
- National Day: September 9th
North Korea’s Population
North Korea has a population of 24,895,000 (World Bank 2013). North Korea has been short of food since the 1990s and has at times been starved of famine. The country is unable to produce enough food for the population, and according to the Red Cross, 16 million North Koreans suffer from chronic food shortages, while 2.8 million need regular food assistance to survive (2013).

Prior to World War II, there was a significant migration flow from the southern parts of Korea to the more industrialized northern peninsula, but this flow was reversed during and after the Korean War in 1950–1953, when an estimated 2 million emigrated from North Korea to South Korea.. The population is ethnically very homogeneous and consists of Koreans, a Mongolian mixture of immigrants in prehistoric times.
The population density averages 206.8 residents per square kilometer (2013), but the settlement is highly concentrated to the coastal areas and to the lowland areas in the southwest. Industrialization after 1945 has made a significant move from the countryside to the cities, and about 60 percent of the population resides in cities and towns against a third in 1950. The largest city is the capital Pyongyang on the Taedong River, about 50 kilometers inland. At the last census in 1993, 2,741,300 residents were registered here. Other important cities are Hamhung – Hungnam and Chongjin, both on the east coast.
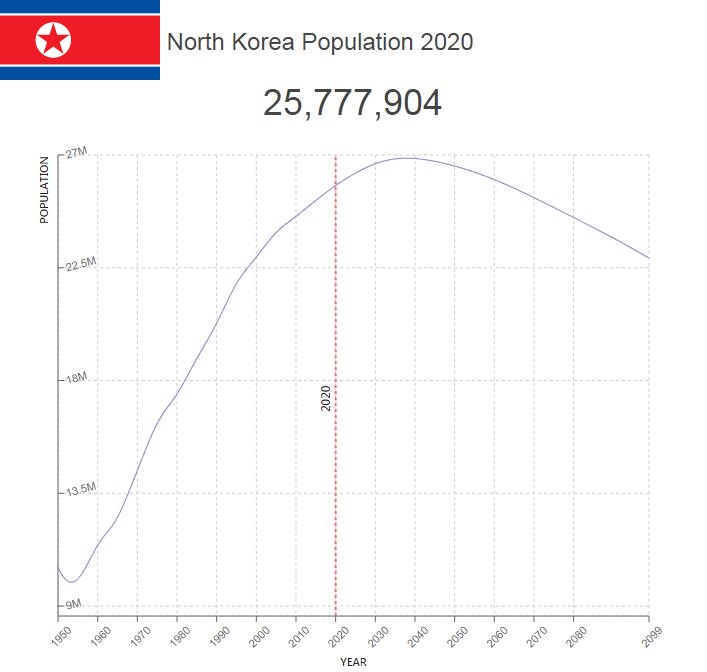
Population of North Korea by Year (Historical)
| Year | Population | Annual Growth Rate | Population Density | Global Rank |
| 2020 | 25,778,705 | 0.440% | 214.0920 | 54 |
| 2019 | 25,666,050 | 0.460% | 213.1564 | 54 |
| 2018 | 25,549,493 | 0.470% | 212.1884 | 52 |
| 2017 | 25,429,714 | 0.480% | 211.1936 | 52 |
| 2016 | 25,307,554 | 0.490% | 210.1791 | 51 |
| 2015 | 25,183,722 | 0.510% | 209.1507 | 51 |
| 2010 | 24,548,725 | 0.530% | 203.8770 | 48 |
| 2005 | 23,904,056 | 0.840% | 198.5231 | 46 |
| 2000 | 22,928,964 | 0.960% | 190.4250 | 45 |
| 1995 | 21,862,188 | 1.500% | 181.5655 | 42 |
| 1990 | 20,292,943 | 1.460% | 168.5330 | 41 |
| 1985 | 18,877,127 | 1.560% | 156.7747 | 40 |
| 1980 | 17,472,029 | 1.430% | 145.1054 | 39 |
| 1975 | 16,274,629 | 2.460% | 135.1610 | 37 |
| 1970 | 14,410,289 | 2.810% | 119.6778 | 37 |
| 1965 | 12,547,414 | 1.890% | 104.2067 | 37 |
| 1960 | 11,424,065 | 2.520% | 94.8773 | 36 |
| 1955 | 10,086,880 | -0.890% | 83.7720 | 36 |
| 1950 | 10,549,361 | 0.000% | 87.6129 | 34 |
Major Cities in North Korea by Population
| Rank | City | Population |
| 1 | Pyongyang | 3,221,889 |
| 2 | Hamhung | 558,945 |
| 3 | Namp’o | 454,889 |
| 4 | Sunch’on | 436,889 |
| 5 | Hungnam | 345,971 |
| 6 | Kaesong | 338,044 |
| 7 | Wonsan | 329,096 |
| 8 | Chongjin | 326,889 |
| 9 | Sariwon | 309,989 |
| 10 | Sinuiju | 288,001 |
| 11 | Haeju | 222,285 |
| 12 | Kanggye | 209,419 |
| 13 | Hyesan | 192,569 |
| 14 | Songnim | 152,314 |
| 15 | Manp’o | 116,649 |
| 16 | P’yongsong | 99,889 |
| 17 | Hyesan-dong | 97,683 |
| 18 | Yuktae-dong | 76,316 |
| 19 | Hongwon | 70,812 |
| 20 | Rajin | 66,113 |
| 21 | Ongjin | 64,136 |
| 22 | Kilju | 63,541 |
| 23 | Chaeryong-up | 53,219 |
| 24 | Anju | 50,085 |
| 25 | Uiju | 49,970 |
| 26 | Hoeryong | 43,720 |
| 27 | Sungho 1-tong | 39,730 |
| 28 | Changyon | 39,257 |
| 29 | Sunan | 36,560 |
| 30 | Hwangju-up | 35,530 |
| 31 | Kyongsong | 35,493 |
| 32 | Aoji-ri | 34,137 |
| 33 | Nanam | 33,944 |
| 34 | Anbyon-up | 31,734 |
| 35 | Kusong | 30,791 |
| 36 | Chongju | 28,954 |
| 37 | Kangdong-up | 28,811 |
| 38 | Sonbong | 27,220 |
| 39 | Iwon-up | 26,253 |
| 40 | Hukkyo-ri | 25,326 |
| 41 | Kosan | 24,711 |
| 42 | Yonan-up | 22,554 |
| 43 | Namyang-dong | 22,107 |
| 44 | Yonggwang-up | 21,771 |
| 45 | Musan-up | 21,628 |
| 46 | Kowon-up | 21,379 |
| 47 | Hoeyang | 21,000 |
| 48 | T’ongch’on-up | 20,464 |
| 49 | Kapsan-up | 20,295 |
| 50 | Anak | 19,884 |
| 51 | Onsong | 19,695 |
| 52 | Kujang-up | 19,411 |
| 53 | Sil-li | 19,352 |
| 54 | Chunghwa | 19,235 |
| 55 | Samho-rodongjagu | 18,914 |
| 56 | Sinmak | 18,558 |
| 57 | Sakchu-up | 17,890 |
| 58 | Ayang-ni | 15,993 |
| 59 | Sinanju | 15,582 |
| 60 | Sinsang-ni | 14,849 |
| 61 | Pukchil-lodongjagu | 14,018 |
| 62 | Hau-ri | 13,470 |
| 63 | Yonggang-up | 13,329 |
| 64 | Pyoksong-up | 12,826 |
| 65 | Koksan | 12,812 |
| 66 | Chasong | 12,625 |
| 67 | Kyongwon | 12,539 |
| 68 | Puryong | 12,156 |
| 69 | Komusan 1-tong | 12,131 |
| 70 | Sungjibaegam | 11,675 |
| 71 | Hoemul-li | 11,570 |
| 72 | Sungam-nodongjagu | 11,295 |
| 73 | Panghyon-dong | 10,915 |
| 74 | Kwaksan | 10,367 |
| 75 | Sangsong-ni | 9,777 |
| 76 | Yongbyon | 9,473 |
| 77 | Yomju-up | 9,326 |
| 78 | Ungsang-nodongjagu | 8,299 |
Religion
According to the Constitution, there is freedom of religion, but religions are suppressed, and somewhat larger organized religious life is unlikely to take place. Around 68 percent are said to be atheists or non-religious. There are followers of traditional religions and Confucianism (about 30 percent) as well as Buddhists and Christians. After the Korean War, some churches and temples have been converted to other uses.
Language
The national language is Korean, which is written with its own alphabet (Hangŭl). The Chinese characters were officially abolished in 1949.













































