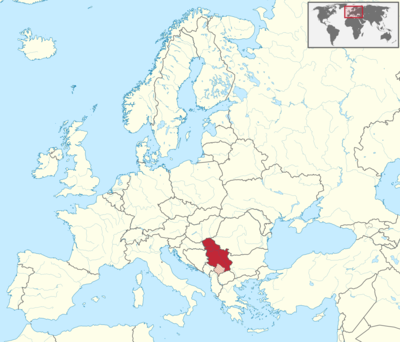
Where is Serbia Located?
Where is Serbia located on the map? Serbia is an independent nation located in Southern Europe. Check out the following images to see location of Serbia on maps.
Serbia Location in World Map
Location Information of Serbia
Serbia is a landlocked country located in Southeast Europe, positioned in the central part of the Balkan Peninsula. Its geographic location places it at the crossroads of Eastern and Western Europe, making it a historically significant region. Serbia is bordered by Hungary to the north, Romania and Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest.
Latitude and Longitude
Serbia is situated at approximately:
- Latitude: 44.0165° N
- Longitude: 21.0059° E
These coordinates place Serbia in the temperate zone, influencing its climate, topography, and overall geographical features.
Capital City and Major Cities
The capital of Serbia is Belgrade, which is also the largest city and the economic, cultural, and political hub of the country. Belgrade lies at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers, offering a rich historical backdrop and strategic position. While Belgrade is the most important urban center, Serbia has other notable cities that contribute to the country’s regional significance and growth.
Major Cities in Serbia:
- Novi Sad: Located in the northern part of the country, Novi Sad is the second-largest city in Serbia. It is the capital of the Vojvodina province and is known for its vibrant cultural scene, particularly the famous EXIT Festival. Novi Sad is also home to the historic Petrovaradin Fortress and offers a mix of urban and rural landscapes.
- Niš: A major city in southern Serbia, Niš is one of the oldest cities in Europe, with a history dating back to Roman times. Niš is strategically located near the borders with Bulgaria and North Macedonia, serving as an important economic and transportation hub.
- Kragujevac: Located in central Serbia, Kragujevac is an industrial city with historical significance, particularly known for being the site of the tragic Kragujevac massacre during World War II. It is also a center for automobile manufacturing and other industries.
- Kraljevo: Positioned in central Serbia, Kraljevo has historical and economic importance, particularly for the region of Raška. The city has a mix of industries, including metalworking and manufacturing.
- Subotica: Situated in the northern part of Serbia near the Hungarian border, Subotica is known for its multicultural heritage and impressive architecture, including its famous Art Nouveau buildings. It is an important economic center in Vojvodina.
Time Zone
Serbia follows the Central European Time (CET), which is UTC +1 during standard time. In the summer months, Serbia observes Daylight Saving Time (DST), switching to Central European Summer Time (CEST), or UTC +2. This change typically begins on the last Sunday in March and ends on the last Sunday in October.
Climate
Serbia has a continental climate, characterized by hot summers and cold winters. The climate varies somewhat across the country due to the differences in altitude and proximity to larger bodies of water like the Danube River.
Seasonal Breakdown:
- Summer (June to August): Summer in Serbia can be quite hot, particularly in the lowland areas such as Vojvodina. Average temperatures during this period range between 25°C (77°F) and 35°C (95°F). The central and southern parts of Serbia experience more intense heat, with occasional heatwaves pushing the temperature above 40°C (104°F).
- Winter (December to February): Winters in Serbia can be cold, with temperatures often falling below freezing, especially in the northern and mountainous regions. Average temperatures in winter range from -2°C (28°F) to 5°C (41°F), though colder spells can see temperatures dip even further. Snowfall is common, particularly in the mountainous areas, which makes Serbia a popular destination for winter sports enthusiasts.
- Spring (March to May): Spring is a transitional season, with temperatures slowly warming up, particularly in April and May. Average temperatures in spring range from 10°C (50°F) to 20°C (68°F). Rain is also more frequent in the spring months, contributing to the lush greenery.
- Autumn (September to November): Autumn brings cooler weather, with temperatures generally ranging between 10°C (50°F) and 20°C (68°F). This season is also marked by the harvest, and the landscape becomes particularly beautiful with the changing colors of the leaves.
Economic Status
Serbia’s economy has undergone significant changes since the 1990s, transitioning from a socialist, state-controlled system to a more market-oriented economy. It is classified as an upper-middle-income country by the World Bank, with the economy showing steady growth in recent years. Serbia has a well-diversified economy, but certain sectors dominate the overall economic landscape.
Key Economic Sectors:
- Agriculture: Agriculture is a significant part of Serbia’s economy, particularly in the fertile plains of the Vojvodina region. Major agricultural products include cereals (such as corn and wheat), fruits (especially raspberries and plums), vegetables, and livestock. Serbia is one of the world’s largest exporters of raspberries, which is one of its most important agricultural exports.
- Manufacturing and Industry: Serbia has a strong industrial base, particularly in the sectors of automotive production, machinery, chemicals, and food processing. Companies like Fiat have established manufacturing plants in Serbia, and the country has become an important hub for automotive production in the region.
- Energy: Serbia is dependent on energy imports, particularly natural gas, but it has a well-developed domestic energy sector, primarily based on coal and hydropower. The country is making efforts to diversify its energy sources, and there is increasing investment in renewable energy technologies.
- Services and Technology: The service sector has seen significant growth, particularly in the fields of telecommunications, banking, and IT services. Belgrade has emerged as a regional hub for IT outsourcing, and Serbia is becoming increasingly known for its growing startup ecosystem. The country’s IT sector is one of the fastest-growing in Europe.
- Tourism: Tourism is an important and expanding industry for Serbia. The country has a lot to offer, including historical landmarks, beautiful landscapes, and vibrant cultural experiences. In recent years, Serbia has seen a rise in both regional and international visitors, drawn by its affordable prices and rich cultural heritage.
Tourist Attractions
Serbia offers a diverse array of attractions, ranging from historical sites to natural wonders. Tourists can enjoy a blend of cultural heritage, scenic landscapes, and vibrant city life.
1. Belgrade:
- Kalemegdan Fortress: A historical landmark located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers. The fortress offers stunning views of the city and the river and is a popular site for both history enthusiasts and casual visitors.
- Republic Square: The heart of Belgrade, featuring important landmarks like the National Museum and the National Theatre.
- Skadarlija: Often referred to as the “Bohemian quarter,” this area is known for its cobbled streets, historic buildings, and vibrant cafes, offering a glimpse into Belgrade’s artistic and cultural past.
2. Novi Sad:
- Petrovaradin Fortress: One of the largest and most impressive fortresses in Europe, it offers panoramic views of Novi Sad and the Danube River.
- EXIT Festival: One of Europe’s biggest music festivals, attracting thousands of visitors from around the world every summer.
- Danube Park: A large and serene park in the heart of the city, perfect for relaxation and leisurely walks.
3. Niš:
- Niš Fortress: A well-preserved Ottoman-era fortress located in the center of Niš.
- Skull Tower: A macabre historical monument built by the Ottomans after the Battle of Cegar, where the skulls of Serbian rebels were used to build a tower.
- Mediana Archaeological Site: The remains of a Roman villa complex and a UNESCO World Heritage site.
4. Tara National Park:
Tara National Park is a pristine natural area, famous for its diverse flora and fauna. It is one of the largest reserves of Serbian Spruce trees, which were thought to be extinct in the wild.
5. Studenica Monastery:
A UNESCO World Heritage site, the Studenica Monastery is one of Serbia’s most important medieval monasteries and an outstanding example of Byzantine architecture.
Visa Requirements for U.S. Citizens
U.S. citizens can visit Serbia without a visa for short stays of up to 90 days within a 180-day period. However, U.S. travelers must meet certain requirements upon entry:
- Passport: A valid U.S. passport with at least 6 months of validity from the date of entry.
- Proof of Accommodation: Proof of booking a hotel or other accommodation.
- Return or Onward Travel Ticket: U.S. citizens must provide evidence of a return ticket or onward travel arrangements.
- Financial Means: Proof of sufficient financial means to support their stay in Serbia, such as cash, bank statements, or credit cards.
For longer stays or purposes other than tourism, such as work or study, U.S. citizens will need to apply for the appropriate visa at the Serbian embassy or consulate.
Distance to Major U.S. Cities
Serbia is located in Southeastern Europe, and the flight times from the United States are substantial.
1. Distance from New York City
The flight distance from New York City (JFK) to Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport (BEG) is approximately 4,800 miles (7,725 kilometers). The flight duration typically takes about 8 to 9 hours direct or with one stop, depending on the route.
2. Distance from Los Angeles
The distance from Los Angeles (LAX) to Belgrade is around 6,000 miles (9,656 kilometers). The flight time is usually between 11 to 13 hours for a direct flight or with one stop, depending on the airline and route taken.
Serbia Facts
| Size | 88,361 km² |
| Residents | 6.9 million |
| Language | Serbian |
| Capital | Belgrade |
| Longest river | Danube (588 km in Serbia) |
| Highest mountain | Midžor (2,169 m) |
| Currency | dinar |