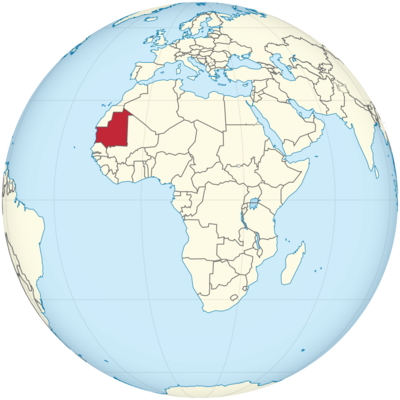
Where is Mauritania Located?
Where is Mauritania located on the map? Mauritania is an independent nation located in Western Africa. Check out the following images to see location of Mauritania on maps.
Mauritania Location in World Map
Mauritania is located in West Africa. Almost the entire country is in the Sahara. The south belongs to the Sahel zone. In the west lies the Atlantic.
The northwest borders with Western Sahara (see Morocco). In the northeast there is a short border with Algeria. The entire east borders on Mali at an angle that seems to have been drawn with a ruler. Senegal is located in the southwest. Mauritania is about three times the size of Germany, but only three million people live here – here it is 82 million!
On the map you can see that Mauritania is in West Africa.
Location Information of Mauritania
Latitude and Longitude
Mauritania is located in the western part of North Africa, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Algeria to the northeast, Mali to the east, and Senegal to the southwest. The country lies between 15.9750° N latitude and 17.0721° W longitude. Its vast desert landscape forms part of the Sahara, while the southern regions are characterized by semi-arid Sahelian terrain, transitioning into more fertile land near the Senegal River.
Capital City and Major Cities
Capital City: Nouakchott
The capital and largest city of Mauritania is Nouakchott, situated on the Atlantic coast. It was founded in 1958 and has since grown to become the political, economic, and cultural center of the country. Nouakchott is located near the edge of the Sahara and serves as a port city on the Atlantic Ocean. As of the most recent estimates, the population of Nouakchott is around 1 million, making it the largest city in Mauritania by far. The city’s economy is based on services, trade, and fishing, with significant infrastructure development in recent years.
Major Cities
- Nouadhibou: Located on the northern coast of Mauritania, near the border with Western Sahara, Nouadhibou is the second-largest city in Mauritania. It serves as the country’s main port for trade and fishing, especially in the fishing industry, and is known for its proximity to the Nouadhibou Bay and important mineral extraction facilities.
- Atar: Situated in the northern part of Mauritania, Atar is an oasis town and a regional administrative center. It is known for its role as a base for exploring the Adrar region, famous for its dunes, ancient towns, and historic sites.
- Kiffa: Located in the southern part of the country, Kiffa is a regional administrative and economic center in the Hodh El Chargui region. Kiffa is known for its traditional crafts, agriculture, and its proximity to the Senegal River.
- Zouerate: In the north, Zouerate is a mining town that serves as the hub for Mauritania’s iron ore industry. The town is located near the Hodh El Gharbi region, which is rich in mineral resources, and it plays a significant role in the country’s mining exports.
- Kaedi: Situated in the south near the Senegal River, Kaedi is an important agricultural and commercial center. The city serves as a key point for regional trade, particularly in crops such as millet, rice, and vegetables.
Time Zone
Mauritania operates on Mauritania Time (GMT), which is UTC +0 year-round. The country does not observe daylight saving time, meaning its time remains constant throughout the year. Mauritania shares the same time zone with several West African countries, including The Gambia and Guinea.
Climate
Mauritania experiences a desert climate in the north and a more semi-arid climate in the south, transitioning into Sahelian conditions. Due to its location on the edge of the Sahara Desert, Mauritania’s weather is predominantly hot and dry, with distinct wet and dry seasons. The country’s climate is significantly influenced by the desert and the harmattan winds, which bring dry air from the Sahara.
- Temperature: The temperature in Mauritania is typically hot year-round, with average daily temperatures ranging from 22°C (72°F) to 35°C (95°F) in the summer months. In the desert regions, daytime temperatures can easily exceed 40°C (104°F) during the hottest part of the year, while the evenings are cooler due to the lack of humidity.
- Rainy Season: The rainy season lasts from June to September, but rainfall is scarce and mainly concentrated in the southern part of the country, particularly around the Senegal River. In these regions, annual rainfall can range from 100 mm (4 inches) to 500 mm (20 inches). In the northern desert regions, however, rain is very rare.
- Dry Season: The dry season, which spans from October to May, is characterized by high temperatures and little to no rainfall. The harmattan winds during the dry season bring dust and hot air from the Sahara, reducing visibility and creating a dry, arid environment throughout the country.
- Dust Storms: Mauritania experiences frequent dust storms, particularly during the dry season, which can reduce air quality and visibility. These storms are common in the desert areas and can affect health and daily activities.
Economic Status
Mauritania has a mixed economy, which combines agriculture, mining, fishing, and services. The country is one of the poorest in the world, but it has a wealth of natural resources, including iron ore, gold, copper, and fisheries. Mauritania’s economic development is constrained by challenges such as limited infrastructure, a lack of diversified industries, political instability, and high poverty rates.
1. Mining
The mining sector is one of the most important contributors to Mauritania’s economy. Mauritania is home to large deposits of iron ore, which accounts for the majority of the country’s exports. The country also produces gold, copper, and phosphates. The mining industry is vital to the country’s revenue, with major operations in the Zouerate and Tasiast mines.
2. Fishing
Fishing is another crucial sector in Mauritania’s economy, providing both food security and income for many Mauritanians. The country’s Atlantic coastline is rich in marine life, particularly fish such as tuna, sardines, and mackerel. Mauritania’s government has worked to develop its fishing industry, and the sector remains one of the largest sources of export revenue. However, overfishing remains a challenge, with foreign fishing fleets operating in Mauritania’s waters.
3. Agriculture
Agriculture in Mauritania is limited by the country’s arid conditions, but it plays an important role in the economy, particularly in the southern regions. The Senegal River provides irrigation for farming, and crops such as millet, sorghum, rice, and vegetables are grown. Livestock farming, particularly cattle, sheep, and camels, also plays a significant role in rural economies.
4. Services and Infrastructure
The service sector is growing, with a focus on banking, telecommunications, and tourism. However, Mauritania’s infrastructure remains underdeveloped, with limited access to electricity and water in rural areas. The country’s transportation network is also limited, and major improvements in road networks and port facilities are required to facilitate trade and economic growth.
5. Poverty and Development Challenges
Despite the presence of rich natural resources, Mauritania remains one of the poorest countries in Africa. The country faces numerous challenges, including high unemployment, low literacy rates, and widespread poverty. A significant portion of the population relies on subsistence farming and pastoralism. Economic inequality, political instability, and social issues such as slavery and human rights abuses continue to hinder development efforts.
Tourist Attractions
While Mauritania’s tourism industry is relatively underdeveloped, the country offers a number of attractions for adventurous travelers interested in history, culture, and the natural environment.
1. Chinguetti
Chinguetti is an ancient city located in the Adrar region and is one of the most significant historical sites in Mauritania. Founded in the 13th century, Chinguetti was once a major center for Islamic learning and trade. The city is home to historic mosques, libraries, and manuscripts, some of which are centuries old. The city itself is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and its location in the desert provides a picturesque backdrop for tourists interested in Mauritania’s history and architecture.
2. The Banc d’Arguin National Park
Located on the Atlantic coast, this UNESCO World Heritage Site is known for its rich biodiversity, particularly birdlife. The park is home to migratory birds, including species like flamingos and pelicans, as well as sea turtles and dolphins. The park’s natural beauty and unique ecosystem make it a popular destination for eco-tourism and birdwatching.
3. The Richat Structure (Eye of the Sahara)
The Richat Structure, also known as the Eye of the Sahara, is a massive circular geological formation located in the desert of southern Mauritania. Its distinctive shape and size make it visible from space. While its origin remains debated, it is believed to be an ancient impact crater or erosion structure. The site is a popular destination for those interested in geology and the mysteries of the desert.
4. Nouakchott Beach
The beaches around Nouakchott provide a relaxing contrast to the country’s arid interior. While not as famous as beaches in other countries, Nouakchott’s coastline offers beautiful sandy shores and is popular for fishing, picnicking, and enjoying the ocean breeze.
5. Oasis Towns and Desert Tourism
Mauritania is home to a number of oasis towns, particularly in the Adrar and Hodh regions, which are often visited by those interested in desert adventures, camel trekking, and experiencing the traditional nomadic way of life. These oasis towns, such as Atar and Ouadane, offer a glimpse into the country’s history and provide a stark contrast to the surrounding desert.
Visa Requirements for U.S. Citizens
U.S. citizens are required to obtain a visa to enter Mauritania. The visa can be obtained either through a Mauritanian embassy or consulate before traveling, or in some cases, upon arrival at Nouakchott International Airport. The visa is typically valid for 30 days and can be extended if necessary. Travelers must present a valid passport, proof of onward travel, and may be required to show evidence of sufficient funds to cover their stay.
Distance to New York City and Los Angeles
Distance to New York City
The distance from New York City to Nouakchott, Mauritania’s capital, is approximately 4,600 miles (7,402 kilometers). There are no direct flights, and travelers typically transit through European or Middle Eastern hubs, such as Paris or Istanbul, before reaching Mauritania.
Distance to Los Angeles
The distance from Los Angeles to Nouakchott is approximately 5,800 miles (9,300 kilometers). Similar to flights from New York, travelers will need to transit through major international airports in Europe or the Middle East before continuing to Mauritania.
Mauritania Facts
| Size | 1,030,700 km² |
| Residents | 4.4 million |
| Languages | Arabic (official language), as well as French and the national languages Fulfulde, Wolof and Soninke |
| Capital | Nouakchott |
| Longest river | Senegal (border river with the country Senegal 813 km) |
| Highest mountain | Kediet Ijill (915 m) |
| Currency | Ouguiya |