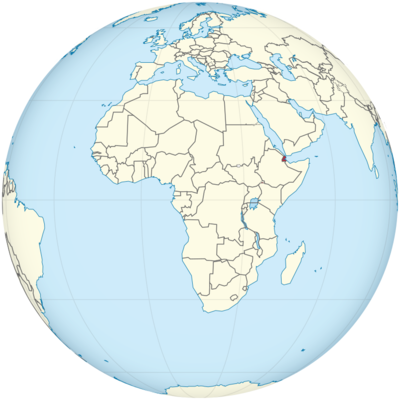
Where is Djibouti Located?
Where is Djibouti located on the map? Djibouti is an independent nation located in Eastern Africa. Check out the following images to see location of Djibouti on maps.
Djibouti Location in World Map
Here you can see where Djibouti is in Africa.
Location Information of Djibouti
Latitude and Longitude
Djibouti is situated in the Horn of Africa, at a strategic location near the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, a vital waterway that connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden. The geographical coordinates of Djibouti are approximately:
- Latitude: 11.8251° N
- Longitude: 42.5903° E
This location places Djibouti at the crossroads of Africa and the Middle East, making it a key point for maritime traffic and regional trade.
Capital City and Major Cities
Capital City: Djibouti City
Djibouti City is the capital and largest city of the country. It serves as the political, economic, and cultural center of Djibouti. The city is located on the coast of the Gulf of Tadjoura, which is a part of the larger Gulf of Aden. The city has a population of approximately 600,000 people, making up a significant portion of the country’s total population.
Other Major Cities:
- Ali Sabieh: Located near the border with Ethiopia, Ali Sabieh is one of the key towns in the southern part of Djibouti. It serves as an important trade and transportation hub for goods moving between Djibouti and Ethiopia.
- Tadjoura: Situated on the western shores of the Gulf of Tadjoura, this is one of the oldest towns in the country. Known for its scenic beauty and proximity to the capital, it plays an important role in Djibouti’s fishing and tourism industries.
- Obock: Located on the northern shores of the Gulf of Tadjoura, Obock is a port city and one of the major commercial centers of Djibouti, dealing mainly with international shipping.
- Doraleh: Located close to Djibouti City, the Doraleh region is home to the Doraleh Multipurpose Port, which has made it an important economic center in the country.
Time Zone
Djibouti operates in the East Africa Time (EAT) zone, which is UTC +3 year-round. Djibouti does not observe Daylight Saving Time (DST), so the time remains consistent throughout the year.
Climate
Djibouti has a desert climate, characterized by high temperatures and very little rainfall throughout the year. The climate is largely influenced by its proximity to the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. The major climate characteristics include:
- Temperature: Djibouti is typically hot year-round. Average temperatures in the capital range from 25°C (77°F) to 40°C (104°F) during the summer months. Even in the cooler months, temperatures rarely fall below 20°C (68°F).
- Rainfall: Djibouti experiences limited rainfall, and much of the precipitation falls during two main seasons: the Gu’ (main rainy season), from March to June, and the Deyr (short rainy season), from October to December. However, the total annual rainfall in most parts of the country is low, often below 200 mm.
- Humidity: The climate is dry and arid, with humidity levels rising near the coast due to the influence of the sea.
- Wind: The region is also known for frequent winds, particularly the Khamaseen, a dry, hot wind that blows from the desert.
Economic Status
Djibouti has a small, service-oriented economy, which is heavily reliant on its strategic location as a global shipping hub and its access to key international maritime routes. Key aspects of Djibouti’s economy include:
- Ports and Trade: The economy of Djibouti is largely dependent on its ports, which serve as a transshipment point for goods moving to and from the Horn of Africa, the Middle East, and Asia. The Port of Djibouti and the Doraleh Container Terminal handle a large amount of international trade, particularly for neighboring landlocked Ethiopia, which relies on Djibouti’s ports for its imports and exports.
- Foreign Military Bases: Djibouti hosts several foreign military bases, most notably those of the United States, France, and Japan, which contribute to the country’s revenue through leases and strategic partnerships. The presence of these bases has also led to Djibouti’s significant role in global security and counter-terrorism efforts.
- Services and Tourism: Djibouti’s services sector, including finance, tourism, and telecommunications, has been growing steadily. Although tourism is still in its infancy compared to many other African nations, Djibouti’s strategic location and scenic beauty are attracting more attention in recent years.
- Agriculture and Fishing: Despite the harsh climate, Djibouti does have some agricultural activity, primarily in the form of livestock farming, such as camels, goats, and sheep. Fishing is also an important industry, particularly in coastal towns like Tadjoura and Obock.
- Challenges: Djibouti’s economy faces challenges such as high unemployment rates, reliance on external trade, and vulnerability to external economic shocks. The country is also heavily dependent on international aid for development projects.
Tourist Attractions
While Djibouti is not as well-known as other tourist destinations, it offers a number of unique attractions for those seeking adventure or a glimpse into the culture and natural beauty of the Horn of Africa.
- Lac Assal: This is one of the lowest points on Earth, located 155 meters (509 feet) below sea level. Lac Assal is a saltwater lake and a popular tourist destination due to its striking white salt flats and stunning scenery. The surrounding volcanic landscape makes it a photographer’s paradise.
- Day Forest National Park: Located in the northwestern part of Djibouti, this park is known for its lush green forests, unique biodiversity, and cool climate. It is an ideal spot for hiking and nature lovers.
- Lake Abbe: A surreal landscape of salt chimneys and hot springs, Lake Abbe is one of the most visually striking places in Djibouti. Its landscape resembles something from another planet, making it a popular site for photographers and adventurers.
- The Gulf of Tadjoura: A marine haven known for its vibrant coral reefs, this gulf offers opportunities for diving and snorkeling. The water is teeming with marine life, including dolphins, whale sharks, and colorful fish.
- Doraleh Multipurpose Port: While the port itself is a vital economic asset for the country, it also offers an interesting look into the commercial side of Djibouti. Visitors can observe the bustling trade activities that contribute to Djibouti’s importance on the global trade map.
- Moucha Island: Located in the Gulf of Tadjoura, this small island is a popular destination for those looking to escape the heat and explore the local marine life. It is a favorite for diving and snorkeling.
Visa Requirements for U.S. Citizens
U.S. citizens who plan to travel to Djibouti need a visa, which can be obtained in several ways:
- Visa on Arrival: U.S. citizens can obtain a visa upon arrival at the airport or at the land border. The visa is usually valid for a stay of up to one month, but it can be extended upon request.
- E-Visa: Djibouti also offers an online visa application process. U.S. citizens can apply for an e-visa through the official Djibouti government website before traveling. This method can save time, as the visa is approved electronically.
- Consular Visa: For longer stays or specific types of visas (e.g., business or multiple entry), U.S. citizens may need to apply for a visa at the nearest Djiboutian embassy or consulate. This process may require additional documentation, such as an invitation letter or proof of travel arrangements.
Visa requirements can change, so travelers are advised to check the most up-to-date information from official sources before making any travel plans.
Distance to New York City and Los Angeles
Djibouti is located in the Horn of Africa, which places it relatively far from the United States. The approximate distances from Djibouti to two major U.S. cities are as follows:
- Distance from Djibouti to New York City: The distance from Djibouti City to New York City is approximately 12,300 kilometers (7,640 miles) in a straight line. Flight durations typically range from 14 to 16 hours, depending on layovers and routes.
- Distance from Djibouti to Los Angeles: The distance from Djibouti City to Los Angeles is about 13,200 kilometers (8,200 miles) in a straight line. Flights usually take around 16 to 18 hours, depending on connections and layover durations.
Djibouti Facts
| Size | 23,200 km² |
| Residents | 850,000 |
| Languages | Arabic and French |
| Capital | Djibouti |
| Longest river | Essalou |
| Highest mountain | Mousa Alli (2,028 m) |
| Currency | Djiboutian Franc |