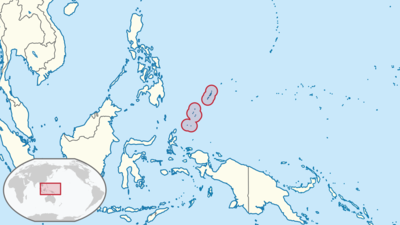
Where is Palau Located?
Where is Palau located on the map? Palau is an independent nation located in Micronesia. Check out the following images to see location of Palau on maps.
Palau Location in World Map
Location Information of Palau
Latitude and Longitude
Palau is an island country located in the western Pacific Ocean, in the region known as Micronesia. It lies at approximately 7.51498° N latitude and 134.58252° E longitude, east of the Philippine Sea. Palau is part of an archipelago that includes over 300 islands, although only about 8 of these islands are inhabited. The country is situated approximately 500 miles (800 km) east of the Philippine Islands and about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) south of Japan.
Palau’s location places it within the tropical zone, offering an abundance of natural resources, including beautiful coral reefs, lush forests, and unique marine life. Its maritime position also provides it with a strategic geopolitical location in the Pacific.
Capital City and Major Cities
Capital City: Ngerulmud
The capital city of Palau is Ngerulmud, located on Babeldaob Island, the largest island in the Palau archipelago. Ngerulmud became the capital in 2006, replacing the former capital, Koror, in an effort to decentralize the government. Ngerulmud is located inland, surrounded by forests and hills, and serves as the administrative center of the country. Despite being the capital, Ngerulmud is relatively small, with a population of about 300 people.
Major Cities
- Koror: The largest and most populous city in Palau, Koror is the country’s main commercial and economic center. It is located on an island of the same name, just off the southern coast of Babeldaob Island. Koror is home to around 11,000 people, which is roughly 70% of the total population of Palau. The city is the hub for tourism, trade, and transportation, with an international airport and several major hotels, restaurants, and shops. Koror is also the primary location for many of Palau’s cultural sites and government buildings.
- Melekeok: Located on Babeldaob Island, Melekeok is a smaller town with a population of around 500. It is situated along the eastern coastline of the island and is near the Ngardmau Waterfall, one of Palau’s famous natural landmarks. Melekeok has been growing in importance since the capital was moved to Ngerulmud, and it remains a key location for those looking to explore the natural beauty of Palau’s largest island.
- Aimeliik: Aimeliik is another town located on Babeldaob Island, in the western part of the island. The town has a population of approximately 1,000 people. It is known for its natural attractions, including hiking trails and scenic beaches. Aimeliik is less developed than Koror and Ngerulmud, but it is an important rural area for agriculture.
- Airai: Airai is another small town located on Babeldaob Island, near Koror. It has a population of around 1,000 people and is known for its agricultural activities, particularly cassava, which is a staple food in Palauan cuisine. Airai also serves as a gateway for visitors traveling to Palau’s famous tourist attractions.
Time Zone
Palau operates on Palau Time (PWT), which is UTC +9:00. This time zone is shared with other countries in the Pacific, such as Japan and South Korea. Palau does not observe Daylight Saving Time, and the time remains the same throughout the year. Palau’s time zone places it ahead of the United States and most countries in Europe.
Climate
Palau has a tropical rainforest climate, characterized by consistently warm temperatures, high humidity, and frequent rainfall year-round. The climate is strongly influenced by its maritime location, making it a year-round destination for those seeking warm weather and natural beauty. The temperature ranges from 77°F to 88°F (25°C to 31°C) throughout the year.
1. Rainy Season (May to November)
The rainy season lasts from May to November, during which Palau experiences the heaviest rainfall. The islands are typically subject to monsoon rains and tropical storms, which bring frequent downpours, particularly in July and August. However, even during the rainy season, rainfall is usually in the form of showers, and there are still many sunny periods during the day. The humid conditions during this season make Palau an ideal destination for those seeking tropical weather, although travelers should be prepared for occasional downpours.
2. Dry Season (December to April)
The dry season runs from December to April, offering drier weather, less humidity, and milder temperatures compared to the rainy season. The dry season is considered the best time to visit Palau, as it has pleasant weather with temperatures ranging from 80°F to 85°F (27°C to 29°C). This period also sees less chance of tropical storms and hurricanes, which is why it is peak tourist season in Palau.
3. Typhoon Risk
Palau is generally considered safe from typhoons compared to other Pacific islands, though typhoons and tropical storms can occasionally affect the region. Typhoons are more common in the central Pacific, and Palau typically experiences less frequent and less intense storms than other parts of the Pacific.
Economic Status
Palau’s economy is relatively small and heavily reliant on tourism, fisheries, and government services. The country has a service-based economy, with significant reliance on foreign aid and the support of the United States, which provides economic assistance through the Compact of Free Association. Palau’s economy is also supported by its natural resources, including marine products and agriculture, but it remains vulnerable to external shocks such as global economic changes, natural disasters, and fluctuations in tourism demand.
1. Tourism
Tourism is the largest sector of the Palauan economy, accounting for around 30-40% of GDP. The country is famous for its pristine beaches, coral reefs, and diverse marine life, making it a popular destination for diving, snorkeling, and eco-tourism. Key attractions for tourists include the Rock Islands, Palau National Marine Sanctuary, and Blue Hole. The tourism industry is also complemented by infrastructure projects and investments in hotels, resorts, and recreational facilities, though the sector is highly dependent on foreign visitors.
2. Fisheries
Fisheries also play a significant role in the Palauan economy, particularly for local consumption and export. Palau’s rich marine resources, including tuna, reef fish, and lobster, contribute significantly to the economy. The Palau National Marine Sanctuary, one of the largest marine protected areas in the world, was established to help preserve marine biodiversity while also supporting sustainable fisheries.
3. Agriculture
While agriculture is not a major contributor to the GDP, it is important for local subsistence. Palau produces a variety of crops, including taro, cassava, coconut, and tropical fruits. The island’s agriculture industry faces challenges such as limited arable land and the impact of climate change, but local agriculture continues to provide food for residents and contribute to the economy.
4. Government Services and Foreign Aid
The government plays a central role in Palau’s economy. The country receives significant economic aid from the United States as part of the Compact of Free Association, which provides financial assistance and allows Palauans to live and work in the United States. Palau’s small population and reliance on public services make the government a key player in the country’s economic development.
5. Challenges
Palau faces challenges in terms of economic diversification, infrastructure development, and maintaining its environmental health. The country’s dependence on tourism makes it vulnerable to external factors like economic downturns and global crises. Climate change also poses risks, particularly to Palau’s marine ecosystems and coastal infrastructure.
Tourist Attractions
- Rock Islands The Rock Islands are one of the most famous attractions in Palau, known for their unique limestone formations and pristine waters. These islands are part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site and offer opportunities for kayaking, snorkeling, and scuba diving. The area is home to coral reefs, marine life, and lush tropical forests, making it a paradise for nature lovers.
- Palau National Marine Sanctuary The Palau National Marine Sanctuary is one of the largest marine protected areas in the world, covering approximately 80% of Palau’s exclusive economic zone. The sanctuary is home to some of the world’s most diverse marine species, including sea turtles, sharks, and coral species. Visitors can enjoy diving and snorkeling in the protected waters, exploring the rich underwater ecosystems.
- The Blue Hole The Blue Hole is a popular diving spot located in the Rock Islands. This underwater sinkhole is famous for its crystal-clear waters and vibrant coral reefs, making it one of the best diving destinations in the world. Divers can explore the depths of the hole and view a wide variety of marine life, including pelagic fish, barracuda, and sea turtles.
- Jellyfish Lake Jellyfish Lake is another popular attraction in Palau, located on Eil Malk Island in the Rock Islands. The lake is home to millions of harmless jellyfish, which have evolved in the lake’s isolated environment. Visitors can snorkel in the lake and swim with the jellyfish, which is an unforgettable experience.
- Babeldaob Island Babeldaob Island is the largest island in Palau and offers a wide variety of natural and cultural attractions. Visitors can explore the Ngardmau Waterfall, hike the island’s trails, and learn about Palauan history and culture at local museums. Babeldaob also offers stunning beaches and lagoons, making it a popular destination for both relaxation and adventure.
Visa Requirements for U.S. Citizens
U.S. citizens do not require a visa for stays of up to one year in Palau. A valid U.S. passport is required for entry, and it must be valid for at least six months beyond the intended departure date. U.S. citizens traveling to Palau for tourism, business, or transit purposes do not need to obtain a visa, but they may need to show proof of return or onward travel.
Distance to New York City and Los Angeles
Distance to New York City
The distance from New York City to Ngerulmud, the capital of Palau, is approximately 10,600 kilometers (6,600 miles). Flights typically take around 16 to 18 hours, depending on layovers and the flight route taken.
Distance to Los Angeles
The distance from Los Angeles to Ngerulmud is approximately 8,500 kilometers (5,280 miles). Flights from Los Angeles typically take around 12 to 14 hours, with layovers commonly in Tokyo, Manila, or Guam.
Palau Facts
| Size | 459 km² |
| Residents | 21,200 |
| Languages | Palauic and English, as well as Japanese and Angaur in Angaur, Sonsorolese on the Sonsorol Islands and Tobian on Tobi |
| Capital | Melekeok |
| Longest river | Ngermeskang River |
| Highest mountain | Mount Ngerchelchuus (242 m) |
| Currency | U.S. dollar |