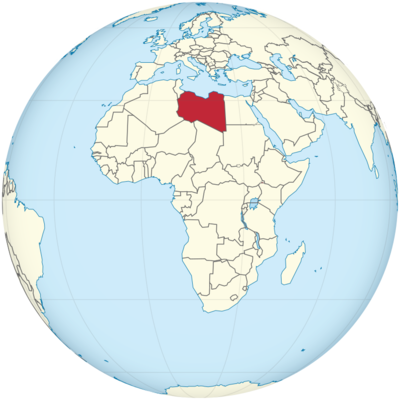
Where is Libya Located?
Where is Libya located on the map? Libya is an independent nation located in Northern Africa. Check out the following images to see location of Libya on maps.
Libya Location in World Map
Libya is in North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean in the north and lies between Algeria and Tunisia in the west and Egypt in the east. There is a short border with Sudan. In the south, Libya borders Niger and Chad.
Libya is the fourth largest country in Africa. Historically it was divided into three provinces: Tripolitania in the northwest, Fezzan in the southwest and Kyrenaica in the east.
The map clearly shows: Libya is in North Africa.
Location Information of Libya
Libya is a country located in North Africa, bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west. As a country of great historical significance, Libya has been at the crossroads of Africa, Europe, and the Middle East for centuries. With its vast desert landscapes, significant oil reserves, and ancient archaeological sites, Libya remains an intriguing destination with a unique geopolitical position.
Latitude and Longitude
Libya lies between approximately 19° and 33°N latitude and 9° and 25°E longitude. The country spans a vast area of over 1.7 million square kilometers (around 700,000 square miles), making it the fourth-largest country in Africa by land area. Libya’s Mediterranean coastline stretches for about 1,770 kilometers (1,100 miles), providing it with significant access to maritime trade routes.
Capital City and Major Cities
Capital City: Tripoli
Tripoli, the capital and largest city of Libya, is located on the Mediterranean coast in the northwestern part of the country. The city has a rich history dating back to antiquity and is known for its strategic importance, historical sites, and cultural heritage. Tripoli is home to approximately 1.1 million people, making it the largest urban center in the country.
Tripoli serves as the political, economic, and cultural hub of Libya. It is the location of key government institutions, commercial activities, and foreign embassies. The city has a blend of modern and historic architecture, with bustling markets, old Ottoman-era buildings, and colonial-era structures. Key landmarks include the Red Castle (Qasr al-Akhbar), the Martyrs’ Square, and the Tripoli Medina.
Major Cities
- Benghazi: Benghazi is the second-largest city in Libya and is located in the northeastern part of the country, along the Mediterranean coast. With a population of around 650,000, Benghazi is an important commercial and industrial center. Historically, the city played a significant role during the Libyan Revolution, and it remains a cultural and intellectual center in the eastern part of the country. Benghazi has experienced significant development in recent years, despite the challenges posed by ongoing political instability and conflict.
- Misrata: Misrata is a coastal city in northwestern Libya, about 200 kilometers east of Tripoli. With a population of over 400,000, it is one of the most economically active cities in the country, particularly in manufacturing, trade, and agriculture. Misrata is also known for its medical facilities and as a key industrial hub. It has played an important role in the recent political landscape of Libya, and it is recognized for its resilience during the 2011 revolution.
- Sirt: Sirt is located along the central Mediterranean coast of Libya, and with a population of approximately 120,000, it is an important city both historically and strategically. The city was the birthplace of Muammar Gaddafi, the former leader of Libya, and it became an epicenter of the civil conflict during the Libyan Civil War. Today, Sirt is rebuilding but remains a city with a significant historical legacy.
- Al-Bayda: Al-Bayda is a city located in the northeastern region of Libya, in the Jabal al-Akhdar mountain range. It has a population of around 100,000 people and serves as an administrative and cultural center in the eastern part of the country. Al-Bayda has a rich cultural history and is known for its role in the Libyan political landscape.
- Zliten: Zliten is a coastal city located approximately 150 kilometers east of Tripoli. The city has a population of about 100,000 and is known for its agricultural output, especially in olive oil production. Zliten also has a significant historical presence and is involved in the ongoing political and social dynamics of the country.
Time Zone
Libya operates on Libya Standard Time (LYT), which is UTC+2. The country does not observe daylight saving time, so the time remains the same throughout the year. This time zone is the same as most countries in the region, including Egypt, Tunisia, and Algeria.
Economic Status
Libya’s economy is heavily dependent on its vast natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas. With some of the largest oil reserves in Africa, Libya has historically been one of the wealthiest countries in the region. However, the economy has faced significant challenges due to political instability, armed conflict, and international sanctions.
- Oil and Natural Gas: Libya has the largest proven oil reserves in Africa, and its economy is primarily driven by the petroleum industry. Oil exports account for about 95% of the country’s revenues, with key export partners including Italy, China, and the United Kingdom. The country has a relatively low oil production capacity compared to other major oil producers, but its oil is high quality and in demand globally.
- Agriculture: Agriculture plays a minor role in Libya’s economy, contributing only around 3-4% of GDP. However, the country does produce some crops such as wheat, barley, olives, and dates. The arid climate and lack of freshwater resources limit agricultural production. Some areas of the country rely on irrigation systems, and there are efforts to improve agricultural efficiency.
- Manufacturing and Industry: Libya’s industrial base is underdeveloped, although the manufacturing sector is growing, particularly in the construction, cement, and chemicals industries. Misrata is a key city for industrial production in Libya, and the government has sought to diversify the economy by promoting manufacturing outside the oil sector.
- Services: The services sector, which includes finance, telecommunications, and tourism, is an important part of the Libyan economy. The telecommunications sector, in particular, has seen significant investment in recent years, though the country still faces challenges in terms of infrastructure development.
- Challenges: Despite its wealth in natural resources, Libya’s economy remains fragile due to ongoing political instability, conflicts, and the destruction of key infrastructure during the civil wars. The conflict has disrupted oil production, limiting the government’s ability to generate revenue. Additionally, international sanctions and low investment levels have slowed the country’s economic recovery.
Tourist Attractions
Libya has a rich historical and cultural heritage, and while tourism has been impacted by political instability, there are several significant attractions that draw travelers interested in archaeology, history, and natural beauty.
1. Leptis Magna
Leptis Magna is one of the most impressive and well-preserved Roman archaeological sites in the world. Located near the coast, about 130 kilometers east of Tripoli, Leptis Magna was once a major city of the Roman Empire. The site includes the remains of a theater, basilica, forum, baths, and a stunning amphitheater. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a major attraction for visitors interested in ancient history.
2. Sabratha
Sabratha, another UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a Roman city located on the Mediterranean coast, about 70 kilometers west of Tripoli. Known for its well-preserved ruins, including a grand theater, temples, and mosaics, Sabratha offers an insight into Libya’s role in the ancient Mediterranean world. The city was once an important center of trade and culture.
3. Ghadames
Ghadames is an ancient oasis town located in the desert region of western Libya, near the borders with Algeria and Tunisia. Known as the “Pearl of the Desert,” Ghadames is famous for its traditional mud-brick architecture and labyrinthine streets. The town is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is a remarkable example of desert architecture.
4. The Sahara Desert
Libya’s vast expanse of the Sahara Desert offers dramatic landscapes, including dunes, rock formations, and ancient caves with prehistoric art. The desert provides opportunities for adventure tourism, including camel treks, off-road tours, and visits to the ancient Berber towns in the desert regions.
5. Tripoli Medina
Tripoli’s Medina is the historic old city of the capital, with narrow streets, traditional souks, and historic buildings dating back to the Ottoman era. The Red Castle (Qasr al-Akhbar) is a prominent landmark, and the Medina offers a glimpse into Libyan culture and history.
6. Cyrene
Cyrene, located in the northeast of Libya, was one of the most important cities of ancient Greece. It boasts significant ruins, including temples, tombs, and a famous theater. The site is another UNESCO World Heritage Site and a valuable place for those interested in ancient Greek civilization.
Visa Requirements for U.S. Citizens
As of 2024, U.S. citizens require a visa to enter Libya for tourism, business, or other purposes. Visa applications must be submitted through the Libyan Embassy or Consulate or through an approved travel agency. The visa process can be time-consuming and requires several documents.
Visa Application Process:
- A valid U.S. passport with at least six months of validity beyond the date of entry.
- A completed visa application form.
- Proof of financial stability, such as bank statements or a letter from a sponsoring organization.
- A visa fee, which typically ranges from $50 to $150.
- A tourist invitation from a Libyan tour operator or business sponsor (if applicable).
- Proof of travel arrangements, such as hotel bookings or flight tickets.
- Health-related documents, such as vaccination certificates (including for yellow fever).
Distance to New York City and Los Angeles
- New York City to Tripoli:
The distance from New York City (JFK) to Tripoli (Mitiga International Airport) is approximately 4,700 miles (7,500 kilometers). Non-direct flights may take 9 to 10 hours, depending on the layover and the route. - Los Angeles to Tripoli:
The distance from Los Angeles (LAX) to Tripoli is about 6,300 miles (10,100 kilometers). A flight from Los Angeles to Tripoli typically takes 12 to 14 hours, depending on the airline and the layover duration.
Mountains
Mountains and highlands with heights of up to 1200 meters can be found on the northern edge of the Sahara, but also in the middle of the desert. Some are of volcanic origin like the Kharuj. In the southeast, the foothills of the Tibesti Mountains from Chad reach Libya. The highest mountain in the country is also located here, the 2267 meter high Bikku Bitt i.
Rivers and Lakes
Few countries in the world do not have permanent rivers. Libya is one of them. There are only wadis here . These are dried up rivers that only carry water after heavy rainfall. Well-known wadis in Libya are, for example, the Wadi al-Ahmar and the Wadi Dinar.
Climate
Libya is one of the hottest countries on earth ! In the Libyan desert there is a drought that is unique in the world. There are places here where no rain has fallen for decades. Temperatures of up to 58 degrees have already been measured, making them one of the places with the highest temperatures ever recorded in the world.
On average in winter it is around 22 degrees during the day, and at night it cools down to around five degrees. In summer it gets 40 degrees during the day, at night it is still around 23 degrees.
It looks different in the Mediterranean. Summers are hot here too, but less hot than in the desert. The winters are mild and humid. The mean temperature in January is 12 degrees, in August 26 degrees. Rain falls mainly between November and February. In spring and autumn, a hot desert wind (Gibli) sometimes blows from the south, bringing sand and dust with it.
Libya Facts
| Size | 1,775,500 km² |
| Residents | 6.67 million |
| Language | Arabic |
| Capital | Tripoli |
| Longest river | – |
| Highest mountain | Bikku Bitti (2,267 m) |
| Currency | Libyan dinar |