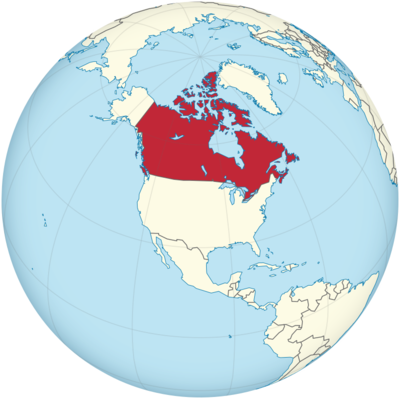
Where is Canada Located?
Where is Canada located on the map? Canada is an independent nation located in North America. Check out the following images to see location of Canada on maps.
Canada Location in World Map
Canada is in North America.
Location Information of Canada
Latitude and Longitude
Canada is the second-largest country in the world by total area, located in North America. It stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the United States border in the south. The vast geography of Canada encompasses a wide range of climates, landscapes, and ecosystems.
- Latitude: 56.1304° N
- Longitude: 106.3468° W
Canada’s vast size, combined with its varying terrain, includes forests, mountains, plains, and coastlines. Its unique geographic position places it within both the Arctic and temperate zones, which influence its climate and environment.
Capital City and Major Cities
- Capital City: OttawaOttawa, located in the eastern part of Ontario, is Canada’s capital city. It is situated on the Ottawa River, near the border of Ontario and Quebec. With a population of about 1 million people, Ottawa is known for its government institutions, museums, and historical landmarks. Ottawa is also home to Parliament Hill, where Canada’s House of Commons and Senate convene.
- Key Features: The Rideau Canal, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is one of Ottawa’s most famous landmarks. In winter, it becomes the world’s largest skating rink. The National Gallery of Canada, Canadian Museum of History, and Parliament Hill are major cultural attractions. The city’s political and cultural influence makes it an important destination for visitors interested in Canadian history and governance.
- Major Cities:
- Toronto: Toronto is the largest city in Canada, located in southern Ontario on the Lake Ontario shoreline. With a population of approximately 3 million people, Toronto is the country’s financial and cultural capital. The city is known for its modern skyline, including the iconic CN Tower, and its multicultural makeup.
- Key Features: The Royal Ontario Museum, Art Gallery of Ontario, and Ripley’s Aquarium are popular cultural attractions. The city also has vibrant neighborhoods such as Chinatown, Little Italy, and Yorkville. As a global financial hub, Toronto is a dynamic metropolis with diverse industries including finance, media, and technology.
- Vancouver: Vancouver, located on the west coast of Canada, is a port city in British Columbia. It has a population of approximately 2.5 million people and is renowned for its natural beauty, offering both mountains and oceans within close proximity. Vancouver is a major economic center, particularly in industries like film production, technology, and shipping.
- Key Features: Stanley Park, the Capilano Suspension Bridge, and Grouse Mountain offer stunning views and outdoor recreation. Vancouver’s climate is milder compared to other parts of Canada, though it still experiences cold winters and rainy seasons. Vancouver is also a key destination for outdoor enthusiasts with opportunities for hiking, skiing, and kayaking.
- Montreal: Montreal, the largest city in the province of Quebec, is a major cultural and financial center. It is the second-largest city in Canada, with a population of about 1.7 million. Montreal is a vibrant, bilingual city, where both French and English are widely spoken.
- Key Features: The Old Port of Montreal, Mount Royal, and Biodome are key attractions. Montreal is known for its diverse culture, thriving arts scene, and festivals like the Montreal International Jazz Festival. The city’s mix of modern and historic architecture, along with its culinary scene, makes it a popular destination for travelers.
- Calgary: Calgary, located in the Alberta province, is a city of approximately 1.2 million people. Known for its proximity to the Rocky Mountains, Calgary is an important business hub, particularly in the oil and gas sectors. The city is also famous for hosting the Calgary Stampede, a massive rodeo and exhibition held every summer.
- Key Features: The Calgary Tower, Canada Olympic Park, and the Heritage Park Historical Village are some of the city’s key attractions. Calgary has a strong western culture, and its surrounding natural landscapes provide ample opportunities for outdoor activities, particularly skiing, hiking, and mountain biking.
- Edmonton: Edmonton, also located in Alberta, is the province’s capital and a major cultural and political center. With a population of around 1 million people, Edmonton is known for its large shopping malls, historical landmarks, and a strong arts community. Edmonton is a gateway to the Northwest Territories and the Yukon.
- Key Features: West Edmonton Mall, one of the largest shopping and entertainment complexes in the world, the Royal Alberta Museum, and Fort Edmonton Park are significant attractions. Edmonton experiences long, cold winters but offers a range of festivals and events year-round, such as the Edmonton International Fringe Theatre Festival.
- Toronto: Toronto is the largest city in Canada, located in southern Ontario on the Lake Ontario shoreline. With a population of approximately 3 million people, Toronto is the country’s financial and cultural capital. The city is known for its modern skyline, including the iconic CN Tower, and its multicultural makeup.
Time Zone
Canada spans six time zones, from Newfoundland Standard Time (NST) in the east to Pacific Standard Time (PST) in the west. These time zones reflect the country’s vast geographic size and the fact that the country spans from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west.
- Newfoundland Standard Time (NST): UTC -3:30
- Atlantic Standard Time (AST): UTC -4
- Eastern Standard Time (EST): UTC -5
- Central Standard Time (CST): UTC -6
- Mountain Standard Time (MST): UTC -7
- Pacific Standard Time (PST): UTC -8
Some provinces, including Ontario, Quebec, and Manitoba, observe Daylight Saving Time (DST) during the summer months, typically from March to November, when clocks are set forward by one hour.
Climate
Canada experiences a diverse range of climates due to its vast size and geographic variation. The country ranges from polar climates in the north to temperate climates in the south.
- Northern Canada (Arctic and Subarctic): The northern regions, including the Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut, have a polar climate with long, harsh winters and very short, cool summers. Temperatures can drop as low as -40°C (-40°F) in winter. The midnight sun is a unique phenomenon in the far north, where the sun does not set for several weeks during summer.
- Eastern and Central Canada (Continental): The prairie provinces (Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba) experience cold winters and hot summers. Winter temperatures can dip below -20°C (-4°F), while summer temperatures can reach 30°C (86°F) or higher. The Great Lakes region experiences a humid continental climate, with cold winters and hot, humid summers.
- Western Canada (Coastal): The west coast of Canada, particularly British Columbia, has a temperate maritime climate. Cities like Vancouver experience mild, wet winters and cool, dry summers. The coastal mountains cause the region to receive heavy rainfall, especially in winter months.
- Southern Canada (Temperate): The southern part of Canada, including cities like Toronto, Ottawa, and Montreal, experiences a humid continental climate with four distinct seasons. Winters are cold, with average temperatures around -10°C (14°F), while summers are warm, averaging 20°C (68°F) to 25°C (77°F). Rain is spread evenly throughout the year.
Economic Status
Canada has a high-income mixed economy, with a combination of private and public sector activity. It is one of the wealthiest countries globally, with a high standard of living, a well-developed infrastructure, and an educated workforce.
- Natural Resources: Canada is a major global producer of oil, natural gas, minerals, and timber. The Alberta oil sands are one of the largest sources of oil in the world, while the country also boasts large reserves of hydroelectric power in its mountainous regions.
- Manufacturing: Canada’s manufacturing sector is diverse, including industries such as automobile manufacturing (mainly in Ontario), aerospace (in Quebec and British Columbia), and electronics. The country also has a strong agriculture industry, producing wheat, canola, and dairy products, among other goods.
- Technology: Canada’s technology sector is growing rapidly, with innovation hubs in cities like Toronto, Vancouver, and Montreal. Software development, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology are key areas of focus.
- Services: The service sector is the largest component of Canada’s GDP, accounting for over 70% of the country’s total economic activity. This includes financial services, healthcare, education, and retail.
- Trade: Canada has strong trade relationships, particularly with the United States, China, and Mexico. The country is a member of several international trade organizations, including the World Trade Organization (WTO) and North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) (now USMCA).
Tourist Attractions
Canada offers a wealth of tourist attractions, from natural wonders to vibrant urban centers:
- Niagara Falls: Located on the border between Ontario and New York, Niagara Falls is one of the world’s most famous natural landmarks, attracting millions of visitors each year.
- Banff National Park: Located in the Canadian Rockies, Banff offers spectacular mountain scenery, hot springs, and abundant wildlife. The Lake Louise area is especially famous for its turquoise waters.
- Old Quebec: A UNESCO World Heritage Site, Old Quebec is a historic district with cobblestone streets, historic buildings, and rich cultural significance. The Château Frontenac is one of the most recognizable landmarks in Canada.
- The Northern Lights: In northern Canada, particularly in the Yukon and Northwest Territories, visitors can experience the breathtaking aurora borealis (Northern Lights), one of nature’s most spectacular phenomena.
- Whistler: A world-class ski resort located near Vancouver, Whistler is famous for its slopes, outdoor recreation, and après-ski culture.
Visa Requirements for U.S. Citizens
U.S. citizens do not need a visa for short visits (tourism, business, or family visits) to Canada for stays up to six months. However, they must carry a valid passport. For stays longer than six months or for work or study, a visa or permit is required.
Distance to New York City and Los Angeles
- Distance to New York City: The distance from Toronto to New York City is approximately 500 miles (800 km), and flights typically take 1.5 hours. For other cities like Montreal or Ottawa, the distance is similarly short.
- Distance to Los Angeles: The distance from Vancouver to Los Angeles is about 1,100 miles (1,770 km). Flights from Vancouver to Los Angeles take approximately 3 hours.
Canada Facts
| Size | 9,984,670 km ² |
| Residents | 37.59 million |
| Languages | English, France |
| Capital | Ottawa |
| Longest river | St. Lawrence River (3,058 km) |
| Highest mountain | Mount Logan (5,959 m) |
| Currency | Canadian dollar |