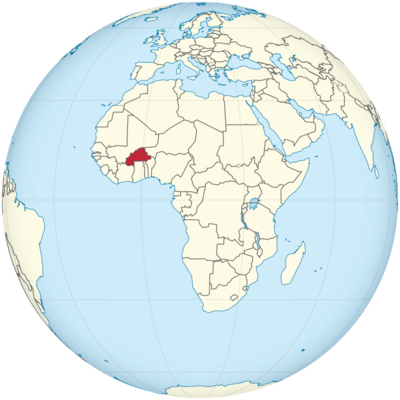
Where is Burkina Faso Located?
Where is Burkina Faso located on the map? Burkina Faso is an independent nation located in Western Africa. Check out the following images to see location of Burkina Faso on maps.
Burkina Faso Location in World Map
Burkina Faso is located in West Africa.
Location Information of Burkina Faso
Latitude and Longitude
Burkina Faso is a landlocked country located in West Africa. It is bordered by six countries: Mali to the north, Niger to the east, Benin and Togo to the south, Ghana to the southwest, and Côte d’Ivoire to the south-west. Its strategic location in the Sahel region of Africa gives it a significant role in West African geopolitics. The country’s geographical coordinates are:
- Latitude: 12.2383° N
- Longitude: 1.5616° W
Burkina Faso’s terrain is predominantly flat with savannahs and occasional hills, making it vulnerable to environmental challenges such as desertification and water scarcity. The country is located just south of the Sahara Desert, which influences its climate and agricultural practices.
Capital City and Major Cities
- Capital City: OuagadougouOuagadougou, the capital city, is located in the central-western part of Burkina Faso. With a population of over 2 million, it is the largest city in the country and serves as its political, cultural, and economic hub. Ouagadougou is known for its vibrant arts scene, bustling markets, and historical sites. The city hosts several festivals, including the FESPACO (Pan-African Film and Television Festival of Ouagadougou), which is one of the most important cultural events in Africa.
Key landmarks in Ouagadougou include the National Museum of Burkina Faso, the Central Market, and the Grand Mosque. The city also features numerous cultural centers, art galleries, and theaters that showcase traditional Burkinabé art and performance.
- Major Cities:
- Bobo-Dioulasso – Located in the western part of the country, Bobo-Dioulasso is the second-largest city in Burkina Faso and an important cultural and commercial center. Known for its historic architecture, particularly in the Dioulassoba Quarter, Bobo-Dioulasso is home to the Grand Mosque, which is one of the largest and most important in the country. The city also hosts an annual festival of traditional music, celebrating the rich musical heritage of Burkina Faso.
- Koudougou – Situated to the west of Ouagadougou, Koudougou is an important regional trade center. The city is known for its agricultural products, particularly cotton, maize, and sorghum, which are staples of the Burkinabé economy. Koudougou has a growing population and a developing infrastructure, and it serves as a gateway for tourists traveling to the Nazinga Game Ranch, a nearby wildlife reserve.
- Banfora – Banfora is a small city located in the southwest, near the Cascades Region. It is a gateway to some of Burkina Faso’s most famous natural attractions, such as the Banfora Waterfalls and the Trek to Sindou Peaks. Banfora also serves as a base for travelers exploring the surrounding nature reserves and national parks.
- Tenkodogo – Tenkodogo, located in the east-central part of the country, is known for its agricultural importance, particularly for millet and groundnut production. The city is also noted for its significant historical sites, including the Tenkodogo Pyramids and the Palace of the Moaga Kings.
- Dori – Situated in the northern part of Burkina Faso, Dori is known for its proximity to the Sahel region, which makes it an important regional trade center. The city acts as a base for exploring the Arli National Park, a major wildlife conservation area in the northeastern part of the country.
Time Zone
Burkina Faso follows Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), which is UTC +0. The country does not observe Daylight Saving Time, and thus, its time zone remains consistent throughout the year. The lack of daylight saving adjustments is typical for many countries in West Africa, and Burkina Faso’s time zone is shared by other countries in the region, such as Mali, Niger, and Ivory Coast.
Climate
Burkina Faso has a tropical climate influenced by its location in the Sahel region, which is characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons. The climate is generally hot and arid, with varying rainfall patterns and temperatures depending on the time of year and geographical region.
- Dry Season (November to March): During the dry season, temperatures are high, ranging from 25°C (77°F) to 40°C (104°F), and the country experiences little to no rainfall. The northern regions of Burkina Faso, especially near the Sahara Desert, can experience extreme heat, with temperatures occasionally rising above 45°C (113°F). The dry season is also marked by the Harmattan winds, which blow in from the Sahara, bringing dust and reducing visibility, particularly in the months of December to February.
- Rainy Season (May to October): The rainy season brings higher humidity and rainfall, particularly in the southern and central parts of the country. Average temperatures during this time range from 20°C (68°F) to 30°C (86°F), but rainfall can significantly reduce the intensity of the heat. The rainy season varies in intensity by region, with the southern areas receiving the most precipitation. Rainfall is crucial for agriculture, which remains the backbone of Burkina Faso’s economy.
- Transition Seasons (April and October): April and October are transitional months, with temperatures still high but with occasional rain showers. These months can be unpredictable, as they represent the shift from the dry season to the wet season, or vice versa. The weather is often humid, and the air quality can be poor due to the combination of dust and rain.
- Vegetation and Wildlife: Due to the climate, Burkina Faso is mostly covered by savannah, which includes both wooded and open areas. The country also has some forested zones in the southwest, but deforestation is a concern. The country’s national parks, such as Arli National Park and W National Park, support various species of wildlife, including elephants, lions, and antelope. Wildlife conservation in these parks is a growing focus for the country’s environmental initiatives.
Economic Status
Burkina Faso is a low-income country with an economy primarily based on agriculture. The country faces significant challenges such as poverty, droughts, and a heavy dependence on foreign aid. However, in recent years, Burkina Faso has made progress in diversifying its economy, with increasing attention to infrastructure development, mining, and services.
- Agriculture: Agriculture employs about 80% of the population, and Burkina Faso is known for its production of cotton, which is one of the largest export commodities. Other major crops include millet, sorghum, maize, rice, and groundnuts. Livestock farming, including cattle and goats, is also an important part of the agricultural economy. However, the sector faces challenges related to erratic rainfall, land degradation, and dependence on outdated farming techniques.
- Mining: Burkina Faso is rich in natural resources, especially gold. In recent years, the mining sector has become a major contributor to the country’s GDP. The country is one of the top gold producers in Africa, and gold mining accounts for a significant portion of export earnings. Other minerals, such as zinc, copper, and manganese, are also important to the economy.
- Services: The services sector is growing in Burkina Faso, particularly in finance, telecommunications, and trade. In the capital city, Ouagadougou, the services sector has expanded with the development of banks, insurance companies, and retail businesses. However, the sector remains underdeveloped compared to more industrialized nations.
- Infrastructure: Despite being a landlocked country, Burkina Faso has developed important transport infrastructure, including road and rail networks that connect to neighboring countries like Mali, Ivory Coast, and Ghana. The road network is generally well-developed in urban areas, but rural regions often face difficulties due to underdeveloped infrastructure. The country is also focusing on improving energy production, with initiatives aimed at expanding access to electricity.
- Challenges: Burkina Faso faces significant challenges, including political instability, particularly in the northern regions near Mali, where terrorist groups operate. The country also struggles with poverty, malnutrition, and inadequate healthcare and education systems. Efforts to address these issues, including development assistance from international organizations, are ongoing.
Tourist Attractions
Burkina Faso, though a less explored tourist destination compared to other African nations, has a unique charm that appeals to travelers interested in culture, history, and nature. Some of the country’s top attractions include:
- Banfora Waterfalls: The Banfora Waterfalls are a series of waterfalls located in southwestern Burkina Faso. The Tanguieta Waterfalls are the most popular among tourists, surrounded by lush vegetation and picturesque scenery. The falls are ideal for hiking, picnicking, and swimming.
- Nazinga Game Ranch: Located in the southern part of Burkina Faso, the Nazinga Game Ranch is a wildlife sanctuary famous for its large population of elephants. The ranch offers safaris where visitors can see a variety of animals, including lions, buffalo, and antelopes.
- Arli National Park: Arli National Park is located in the eastern part of Burkina Faso, near the border with Niger. The park is home to a variety of wildlife, including elephants, lions, leopards, and baboons. The park also features savannahs, acacia woodlands, and wetlands.
- W National Park: This UNESCO World Heritage site is shared between Burkina Faso, Niger, and Benin. The park is home to diverse wildlife and bird species, making it a haven for nature lovers and wildlife photographers.
- Ouagadougou Grand Market: The Grand Market of Ouagadougou is a bustling center where tourists can buy traditional crafts, fabrics, jewelry, and food. It is a great place to experience the local culture and purchase souvenirs.
Visa Requirements for U.S. Citizens
U.S. citizens traveling to Burkina Faso are required to obtain a visa prior to arrival. The following documents and requirements are necessary for a visa application:
- Visa Application Form: A completed visa application form is required for all travelers.
- Passport: A valid U.S. passport with at least six months of validity beyond the date of entry.
- Visa Fee: The visa fee depends on the duration of stay and type of visa (single-entry or multiple-entry).
- Proof of Funds: Travelers may be asked to show evidence of sufficient funds to cover their stay in the country.
- Return Ticket: U.S. citizens will need to show proof of return or onward travel.
Travelers can apply for a visa through the Embassy of Burkina Faso in Washington, D.C., or consular offices.
Distance to Major U.S. Cities
- Distance to New York City: The approximate distance from Ouagadougou to New York City is 5,000 miles (8,000 kilometers). Flights generally take 9-11 hours, with at least one stopover, commonly in European hubs such as Paris or Amsterdam.
- Distance to Los Angeles: The distance from Ouagadougou to Los Angeles is approximately 6,000 miles (9,650 kilometers). Flights typically take 12-14 hours, with layovers in European or Middle Eastern cities such as Paris or Doha.
Burkina Faso Facts
| Size | 274,000 km² |
| Residents | 19.75 million |
| Language | French (official language) |
| Capital | Ouagadougou |
| Longest river | Mohoun (Black Volta, in Burkina Faso approx. 700 km) |
| Highest mountain | Tena Kourou (749 m) |
| Currency | CFA franc |