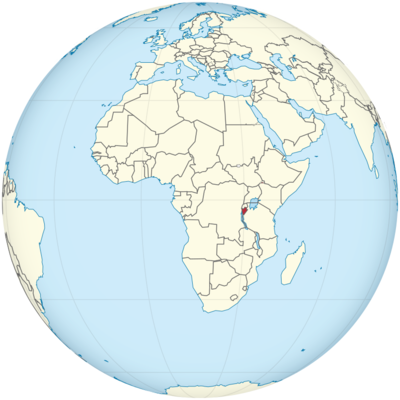
Where is Burundi Located?
Where is Burundi located on the map? Burundi is an independent nation located in Eastern Africa. Check out the following images to see location of Burundi on maps.
Burundi Location in World Map
Burundi is in the east of Africa.
Location Information of Burundi
Latitude and Longitude
Burundi is a landlocked country located in East Africa. It lies in the central part of the African continent, sharing borders with Rwanda to the north, Tanzania to the east and south, and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) to the west. The country’s geographical coordinates are:
- Latitude: 3.3731° S
- Longitude: 29.9189° E
Burundi’s position places it in the heart of the East African region, with diverse landscapes ranging from hills and plateaus to lakes and forests. Its central location also connects it to the Great Lakes region, which is crucial for trade and cultural exchange.
Capital City and Major Cities
- Capital City: Bujumbura (now Gitega is the official political capital)Burundi’s capital city, Bujumbura, was the political and economic center of the country until 2019. However, in 2019, the Burundian government officially moved the capital to Gitega as part of a national effort to decentralize governance and promote development in other regions of the country. Bujumbura remains the economic hub due to its port on Lake Tanganyika and its strategic location for trade.
- Bujumbura: Bujumbura is situated on the western shore of Lake Tanganyika, Africa’s second-largest freshwater lake. The city is an important center for commerce, particularly trade in fish, coffee, and other agricultural products. It has a vibrant market culture, a bustling port, and is a place for tourists to explore traditional music and culture. The city is also home to many international organizations and embassies.
- Gitega: The new political capital of Burundi, Gitega, is located in the central part of the country. It is smaller than Bujumbura but is growing rapidly in terms of infrastructure and governmental importance. Gitega has a more laid-back atmosphere and is known for its traditional architecture and surrounding natural beauty.
- Major Cities:
- Ngozi: Located in the northern part of the country, Ngozi is Burundi’s third-largest city. It is an agricultural hub known for producing crops like maize, beans, and cassava. The city is surrounded by scenic hills and is considered one of the country’s more tranquil places.
- Muyinga: Located in the northeastern part of Burundi, Muyinga is another significant town, serving as an agricultural center for the surrounding region. The city is known for its beautiful hills and fertile lands that produce crops like corn, sweet potatoes, and cassava.
- Ruyigi: Situated in the eastern part of the country near the border with Tanzania, Ruyigi is an important regional city. It has a burgeoning market economy and plays a key role in trade, especially in agricultural products.
- Cibitoke: Located in the western part of Burundi, near the border with the Democratic Republic of Congo, Cibitoke is a city known for its diverse flora and fauna. Its proximity to Lake Tanganyika makes it an essential center for regional trade and transportation.
- Kayanza: Located in the northern highlands, Kayanza is a city known for its agricultural activities, particularly coffee production. Coffee is a key export product for the country, and Kayanza is one of the key regions for high-quality beans.
Time Zone
Burundi operates in the Central Africa Time Zone (CAT), which is UTC +2. The country does not observe Daylight Saving Time, so the time zone remains consistent year-round. This time zone is the same as that of other countries in the region, such as Tanzania, Uganda, Kenya, and Zambia.
Climate
Burundi has a tropical climate, characterized by two distinct seasons: a wet season and a dry season. The climate is influenced by the country’s elevation, as much of the country is covered by plateaus and hills. The climate is also affected by the proximity to Lake Tanganyika, which contributes to more moderate temperatures along the lake shore.
- Wet Season (October to April): The wet season in Burundi is marked by higher humidity and rainfall, especially in the central and western parts of the country. The heaviest rains usually occur between November and March, while April marks the end of the rainy period. This season is critical for agriculture, particularly for crops such as coffee, bananas, and maize. Average temperatures during the wet season range from 18°C (64°F) to 26°C (79°F), but it can be cooler in the higher elevations.
- Dry Season (May to September): The dry season lasts from May to September and is generally characterized by cooler and more comfortable temperatures, particularly in the highland areas. Temperatures during the dry season typically range from 17°C (63°F) to 26°C (79°F). However, the region around Lake Tanganyika remains warmer and more humid compared to the inland plateaus.
- Regional Variations: The climate in Burundi varies by altitude. The highland regions (such as the northern and central areas) have a more temperate climate, while the lowland regions near the shores of Lake Tanganyika experience a more tropical climate with higher humidity and warmer temperatures year-round.
- Vegetation: Due to the tropical climate, Burundi has a rich diversity of vegetation, including dense forests in the west, grasslands, and agricultural land. Coffee and tea are the most important crops cultivated in the fertile highlands. Additionally, the country is home to a variety of wildlife, especially in the eastern and southern areas.
Economic Status
Burundi remains one of the poorest countries in the world, with a predominantly agrarian economy. Agriculture forms the backbone of the economy, with coffee, tea, and agricultural products being the key exports. However, the economy faces numerous challenges such as political instability, poverty, and landlocked geography. Burundi also faces significant environmental pressures, including soil degradation, deforestation, and the effects of climate change.
- Agriculture: The agricultural sector is critical to Burundi’s economy, employing over 90% of the population. The country is known for producing high-quality coffee, which is one of its most important exports. Tea, cassava, sweet potatoes, and maize are also significant crops. However, the sector is vulnerable to fluctuations in weather patterns and lacks modern agricultural techniques, which limits productivity.
- Mining: While Burundi has significant natural resources, including minerals such as tin, tungsten, gold, and nickel, the mining sector is underdeveloped. The government has made efforts to attract investment in mining, but the industry faces challenges such as political instability and inadequate infrastructure.
- Infrastructure: Burundi’s infrastructure is underdeveloped, particularly in rural areas. The country’s transport network (including roads, rail, and ports) is inadequate for the needs of the economy, and the energy sector faces significant constraints. The lack of modern infrastructure hinders economic growth and foreign investment.
- Human Development: Despite recent efforts to reduce poverty, Burundi remains one of the least developed countries globally. Challenges such as political instability, a lack of access to quality healthcare and education, and the consequences of civil conflict continue to hinder development. However, international organizations and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are active in providing humanitarian aid and supporting development projects.
Tourist Attractions
Burundi, while not a major tourist destination compared to some other African countries, offers unique attractions that appeal to those interested in culture, nature, and history. Some of the country’s notable tourist destinations include:
- Lake Tanganyika: Burundi’s western border is defined by the shores of Lake Tanganyika, one of the deepest and oldest lakes in the world. The lake is known for its stunning beaches, vibrant fishing communities, and opportunities for water-based activities, including fishing, boating, and swimming. The lakeside town of Bujumbura offers a variety of accommodations and serves as a starting point for exploring the lake.
- Rusizi National Park: Located near Lake Tanganyika, Rusizi National Park is a popular spot for nature lovers. The park is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including hippopotamuses, crocodiles, and numerous bird species. Visitors can enjoy boat tours along the Rusizi River and explore the park’s rich ecosystems.
- Kibira National Park: Kibira is one of Burundi’s most important national parks, located in the northwest of the country. The park is known for its rainforests, biodiversity, and scenic landscapes. It is a habitat for primates, including chimpanzees and monkeys, and offers hiking and nature walks.
- Gishora Drum Sanctuary: Gishora, located in the central part of Burundi, is famous for its traditional Burundian drumming culture. The Gishora Drum Sanctuary is a place where visitors can experience live performances of the traditional Burundian drum ensembles and learn about the history and significance of drumming in the country’s culture.
- Bujumbura’s Museums and Markets: The city of Bujumbura offers a variety of cultural and historical sites, such as the Burundi National Museum, where visitors can learn about the country’s history, and the Grand Marché, a vibrant marketplace where local goods, including artisan crafts and traditional fabrics, are sold.
Visa Requirements for U.S. Citizens
U.S. citizens wishing to travel to Burundi must obtain a visa prior to arrival. The following documents and requirements are necessary for the visa application:
- Visa Application: A completed visa application form is required.
- Passport: A U.S. passport that is valid for at least six months from the intended date of arrival.
- Visa Fee: Visa fees vary based on the type of visa and length of stay.
- Proof of Funds: U.S. citizens may be asked to show evidence of sufficient funds to cover their stay in the country.
- Return Ticket: Proof of a return or onward travel ticket may be required.
- Vaccination Certificate: U.S. citizens traveling to Burundi may need to show proof of yellow fever vaccination.
Visas can be obtained through the Embassy of Burundi or consular offices.
Distance to Major U.S. Cities
- Distance to New York City: The distance between Bujumbura (or Gitega) and New York City is approximately 7,500 miles (12,000 kilometers). The flight duration is typically around 16-18 hours, with layovers in European or Middle Eastern hubs such as Istanbul, Paris, or Doha.
- Distance to Los Angeles: The distance from Bujumbura (or Gitega) to Los Angeles is about 8,000 miles (12,875 kilometers). Flights typically take around 18-20 hours, with layovers in European or Middle Eastern cities such as Dubai or Paris.
Burundi Facts
| Size | 27,834 km² |
| Residents | 12 million |
| Languages | Kirundi and French |
| Capital | Bujumbura |
| Longest river | Ruvubu (total length 380 km) |
| Highest mountain | Mont Heha (2,684 m) |
| Currency | Burundi Franc |