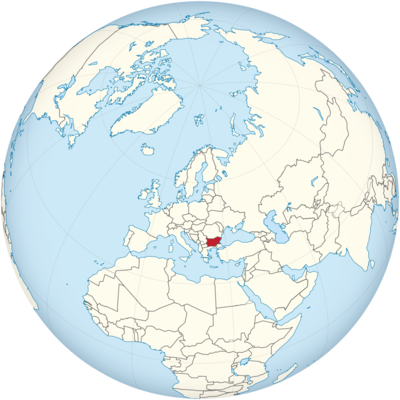
Where is Bulgaria Located?
Where is Bulgaria located on the map? Bulgaria is an independent nation located in Eastern Europe. Check out the following images to see location of Bulgaria on maps.
Bulgaria Location in World Map
Where is Bulgaria located on the map? Bulgaria is located in the southeast of Europe.
Location Information of Bulgaria
Latitude and Longitude
Bulgaria is a country located in Southeast Europe, on the Balkan Peninsula. It is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. The geographical coordinates of Bulgaria are:
- Latitude: 42.7333° N
- Longitude: 25.4858° E
These coordinates place Bulgaria in a geographically diverse region, with mountains in the west, plains and river valleys in the central part, and a coastline along the Black Sea to the east. This strategic location has historically made Bulgaria an important crossroads for trade and cultural exchange between Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
Capital City and Major Cities
- Capital City: SofiaSofia, the capital of Bulgaria, is located in the western part of the country, near the foothills of Mount Vitosha. With a population of over 1.2 million, it is the largest city in Bulgaria and the political, economic, and cultural center of the country. Sofia’s history dates back over 2,000 years, with traces of Roman, Ottoman, and Byzantine influence visible in its architecture and cultural heritage. Key landmarks in Sofia include the Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, the National Palace of Culture, the Boyana Church (a UNESCO World Heritage site), and Vitosha Boulevard, a popular shopping street.
- Major Cities:
- Plovdiv – Located in central Bulgaria, Plovdiv is the country’s second-largest city and one of the oldest continually inhabited cities in Europe. It is known for its rich cultural history, which spans over 6,000 years. Plovdiv features Roman ruins, including the Roman Theater, the Ancient Stadium, and the Djumaya Mosque. The city is also known for its vibrant arts scene, with the Kapana District being a center for creativity and culture.
- Varna – Situated on the Black Sea coast, Varna is the third-largest city in Bulgaria and the country’s main port. Varna is a popular summer tourist destination, known for its beaches, parks, and historical landmarks, such as the Varna Archaeological Museum, the Sea Garden, and the Aladzha Monastery. The city also hosts various cultural events, including the Varna Summer International Music Festival.
- Burgas – Located in southeastern Bulgaria, along the Black Sea coast, Burgas is an important industrial, transport, and tourist city. It is known for its beaches, including Sunny Beach and Nessebar, as well as its beautiful parks and lakes. Burgas also serves as a gateway to nearby resorts and natural attractions, such as the Ropotamo Nature Reserve.
- Ruse – Situated on the Danube River in the northern part of Bulgaria, Ruse is the country’s fifth-largest city and a major transport hub. Known as the “Little Vienna” due to its Austrian-style architecture, Ruse is rich in cultural heritage, with landmarks like the Ruse Regional Historical Museum, Sveta Troitsa Church, and Danube Park.
- Stara Zagora – Located in central Bulgaria, Stara Zagora is one of the oldest cities in the country, with a history that dates back to Thracian times. It is known for its rich archaeological sites, such as the Roman Forum and the Yagodina Cave, as well as its extensive green spaces, including Bedechka Park.
Time Zone
Bulgaria operates on Eastern European Time (EET), which is UTC +2. During the summer months, Bulgaria observes Eastern European Summer Time (EEST), which is UTC +3. The time zone is shared by several other countries in Eastern Europe, including Greece, Romania, and Turkey. The country switches to daylight saving time from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October.
Climate
Bulgaria has a continental climate, characterized by hot summers, cold winters, and distinct seasonal changes. The country’s climate is influenced by its geographical location, with varying conditions in different regions of the country due to its diverse topography.
- Winter: Winters in Bulgaria are cold, with average temperatures ranging from -5°C (23°F) to 5°C (41°F) in most regions. The mountainous areas in the west experience colder temperatures and more snowfall, making it an ideal destination for winter sports such as skiing and snowboarding. Snowfall is common, particularly in the higher altitudes of places like Bansko, Borovets, and Pamporovo.
- Summer: Summers are hot, particularly in the southern and lowland regions. Average temperatures during the summer range from 20°C (68°F) to 30°C (86°F), but they can occasionally exceed 35°C (95°F) during heatwaves. The coastal areas, especially in Varna and Burgas, benefit from the cooling effects of the Black Sea, making them popular beach destinations during the summer months.
- Spring and Autumn: Both spring and autumn are mild and pleasant, with temperatures ranging from 10°C (50°F) to 20°C (68°F). Spring sees an influx of flowers and greenery, while autumn brings vibrant fall foliage. These transitional seasons are ideal for outdoor activities, such as hiking and exploring Bulgaria’s national parks.
- Rainfall: The northern and central regions of Bulgaria tend to receive more precipitation, especially in the spring and early summer. The Struma River Valley and Pirin Mountains experience higher rainfall compared to the rest of the country, contributing to lush vegetation. The coastal regions of Bulgaria, particularly along the Black Sea, receive moderate rainfall, with the wettest months typically being May to June.
Economic Status
Bulgaria has a developing economy with a strong focus on services, industry, and agriculture. The country transitioned from a centrally planned economy under communist rule to a market economy after the collapse of the Soviet Union. While the country has made significant progress, challenges such as income inequality, an aging population, and reliance on foreign investment remain.
- Agriculture: Agriculture has traditionally been an important sector in Bulgaria’s economy. The country produces a variety of crops, including wheat, corn, tobacco, and sunflower seeds. Bulgaria is also known for its production of high-quality fruits and vegetables, particularly roses for essential oils and grapes for wine production. The country is one of the largest wine producers in Eastern Europe, and Bulgarian wines are gaining international recognition.
- Industry: Bulgaria has a well-established industrial base, particularly in machinery, chemicals, and metallurgy. The country is known for its production of machinery, automobile parts, and electronics. The steel industry plays a significant role in the economy, with Kremikovtsi Steel Mill being one of the largest producers in the region. Bulgaria also has a growing information technology sector, with software development, outsourcing, and innovation hubs emerging, particularly in Sofia.
- Services: The services sector has become increasingly important to the Bulgarian economy. Tourism, retail, finance, and real estate have expanded in recent years, contributing to GDP growth. The financial services sector is growing, with banking institutions such as UniCredit Bulbank and Raiffeisenbank playing key roles. Sofia is a growing financial hub for the Balkans, with several international corporations and tech startups establishing offices in the capital.
- Energy: Bulgaria is largely dependent on fossil fuels for energy production, with significant reliance on coal, nuclear energy, and natural gas. The country is home to the Kozloduy Nuclear Power Plant, which provides a large portion of the country’s electricity. Bulgaria is working on expanding its renewable energy capacity, particularly in solar and wind energy.
- Tourism: Tourism is a growing industry, with increasing numbers of visitors attracted by the country’s natural beauty, cultural heritage, and historical landmarks. Bulgaria is known for its ski resorts, such as Bansko and Borovets, as well as its Black Sea coast, including the cities of Varna and Burgas. Cultural and historical tourism is also popular, with the Rila Monastery, Plovdiv’s Roman Theater, and Nessebar’s ancient ruins being key attractions. The UNESCO World Heritage sites in Bulgaria, including Boyana Church and Thracian Tombs, further bolster its tourism sector.
- Challenges: Despite its economic progress, Bulgaria faces several challenges. These include a shrinking labor force due to emigration and an aging population, slow legal reforms, income disparity, and corruption. Bulgaria’s reliance on exports and foreign direct investment makes it vulnerable to global economic changes. However, EU membership since 2007 has provided the country with access to European markets and financial support, helping to stabilize the economy.
Tourist Attractions
Bulgaria is a country rich in cultural heritage, natural beauty, and history, offering a wide range of attractions for visitors. Some of the top tourist destinations include:
- Rila Monastery: The Rila Monastery, located in the Rila Mountains, is one of Bulgaria’s most important cultural and religious sites. A UNESCO World Heritage site, the monastery is known for its stunning frescoes, architectural beauty, and serene location amidst the mountains. It is a significant pilgrimage site for Orthodox Christians and a popular destination for visitors seeking peace and tranquility.
- Plovdiv Old Town: Plovdiv, one of the oldest cities in Europe, is known for its well-preserved Roman ruins, including the Roman Theater, Roman Stadium, and Ancient Agora. The city’s Old Town is a UNESCO World Heritage site, with cobbled streets, colorful houses, and traditional Bulgarian architecture. Plovdiv is also known for its vibrant arts and music scene, especially during the annual Plovdiv International Fair.
- Nessebar: Located on the Black Sea coast, Nessebar is a UNESCO World Heritage site famous for its medieval architecture, ancient ruins, and picturesque location on a small peninsula. Visitors can explore its ancient churches, such as the Church of St. John the Baptist and the Church of Christ Pantocrator, and enjoy the beaches and seaside atmosphere.
- Bansko: Bansko is one of Bulgaria’s most popular ski resorts, located in the Pirin Mountains. The resort offers world-class ski slopes, hiking trails in the summer, and vibrant apres-ski activities. The town of Bansko itself has a charming historical center with cobblestone streets and traditional Bulgarian houses, and it is known for its cultural festivals, including the Bansko Jazz Festival.
- Thracian Tomb of Kazanlak: This UNESCO World Heritage site is an ancient burial tomb dating back to the 4th century BC. The tomb is famous for its well-preserved frescoes depicting scenes from Thracian life and rituals. It is located in the Valley of the Roses, a region known for its beautiful landscapes and rose cultivation.
- The Black Sea Coast: Bulgaria’s Black Sea coast is dotted with popular resorts, such as Varna, Burgas, and Golden Sands, offering beaches, resorts, and vibrant nightlife. The coast is also home to natural parks, historic sites, and picturesque fishing villages.
- Belogradchik Rocks: Located in the northwestern part of Bulgaria, the Belogradchik Rocks are a unique natural formation consisting of rock formations and caves. The area is part of the Belogradchik Rocks Nature Reserve and is a popular destination for hiking, photography, and exploring ancient fortresses.
Visa Requirements for U.S. Citizens
U.S. citizens traveling to Bulgaria for tourism do not require a visa for stays of up to 90 days within a 180-day period. However, the following requirements apply:
- Passport: U.S. citizens must have a valid U.S. passport with at least six months of validity beyond the date of entry.
- Proof of Sufficient Funds: Travelers may be asked to show proof of sufficient funds to cover their stay.
- Return or Onward Travel: U.S. citizens must provide evidence of a return or onward travel ticket when entering the country.
For stays longer than 90 days, U.S. citizens will need to apply for a visa or residence permit through the Embassy of Bulgaria or Consulate.
Distance to Major U.S. Cities
The approximate distances from Sofia, Bulgaria, to major U.S. cities are:
- Distance to New York City: The distance from Sofia to New York City is approximately 5,150 miles (8,290 kilometers). Flights typically take about 9-10 hours, with one or more layovers in major European cities such as Frankfurt or London.
- Distance to Los Angeles: The distance from Sofia to Los Angeles is approximately 6,200 miles (10,000 kilometers). Flights generally take around 12 hours, with layovers typically occurring in Vienna, Munich, or London.
Bulgaria Facts
| Size | 110,994 km² |
| Residents | 6.96 million |
| Language | Bulgarian |
| Capital | Sofia |
| Longest river | Danube (length in Bulgaria 500 km) |
| Highest mountain | Musala (2,925 m) |
| Currency | Lev |