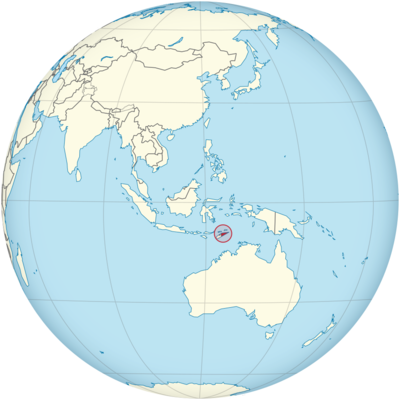
Where is East Timor Located?
Where is East Timor located on the map? Timor-Leste is an independent nation located in Southeastern Asia. Check out the following images to see location of East Timor on maps.
East Timor Location in World Map
On the map you can see the location of East Timor. Indonesia occupies the western part of the island of Timor.
Location Information of East Timor
East Timor, officially known as the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is a small island nation located in Southeast Asia. It lies in the Malay Archipelago on the eastern half of the island of Timor, and is bordered by Indonesia to the west and the Timor Sea to the north. The country is positioned in a geopolitically significant area, close to Australia and several other Pacific nations.
Latitude and Longitude
East Timor is located between 8° and 10° S latitude and 125° and 127° E longitude. This strategic positioning places the country within the tropics, contributing to its tropical climate, while its location near major sea routes impacts its historical and contemporary trade relations.
- Latitude: The country extends between 8° S and 10° S, lying just south of the equator, which affects its weather patterns and the type of flora and fauna found there.
- Longitude: Spanning from 125° E to 127° E, East Timor is situated on the eastern edge of the Timor Sea, with waters surrounding the island contributing to its biodiversity and trade connections.
Capital City and Major Cities
The capital of East Timor is Dili, which is also the largest city in the country. Dili serves as the political, economic, and cultural center of the nation. Other important cities in the country include Baucau, Liquiçá, and Maliana, each of which holds significance in terms of geography, history, or administrative importance.
Dili
Dili, located on the north coast of the island of Timor, is East Timor’s bustling capital and primary urban center. The city sits on the edge of a deep harbor, surrounded by mountains, and is the hub of government, commerce, and culture in the country.
- Economy: Dili serves as the economic center of East Timor. The city is home to the country’s key industries, including oil and gas, fishing, and tourism. The presence of natural resources, particularly offshore oil fields, plays a significant role in the city’s economy.
- Culture and Landmarks: Dili is home to various cultural institutions, including the National Museum of Timor-Leste and Santa Cruz Cemetery, which holds historical significance due to the 1991 massacre. The Cristo Rei statue, which stands at 27 meters tall, is one of the most prominent landmarks in Dili, symbolizing both Catholicism and national pride.
Baucau
Baucau is the second-largest city in East Timor and is located on the eastern coast of the island. Historically, it served as the capital during the Portuguese colonial period, before Dili took over that role.
- Economy: Baucau is important for agriculture, particularly the cultivation of coffee, which is one of East Timor’s main exports. The city also serves as a hub for trade and logistics in the eastern region of the country.
- Culture and Landmarks: Baucau features colonial-era buildings, traditional markets, and stunning coastal scenery. The Baucau Beach is a popular location for both locals and tourists looking to enjoy the natural beauty of the area.
Liquiçá
Liquiçá is a small town located on the northern coast of East Timor, about 30 kilometers west of Dili. The town is historically significant for its involvement in the country’s struggle for independence.
- Economy: The economy of Liquiçá is centered around agriculture, including crops such as coconuts, cassava, and coffee. There is also some involvement in local fishing activities.
- Culture and Landmarks: Liquiçá is an important historical site as it was one of the locations affected by the Indonesian military operations during the struggle for independence. The town is a gateway to the surrounding hills and has several beaches with good diving opportunities.
Maliana
Maliana is a small town located in the western part of the country, near the border with Indonesia. It plays an important role in East Timor’s agricultural sector, and its location close to the border also makes it important for trade.
- Economy: The area around Maliana is known for its fertile agricultural land, growing products like rice, corn, and coffee.
- Culture and Landmarks: Maliana is less developed compared to Dili but provides a more traditional experience of East Timor, with nearby rural areas that showcase the indigenous lifestyle and customs of the Timorese people.
Time Zone
East Timor is located in the East Timor Time (TLT) zone, which is UTC +9:00. This time zone places the country ahead of many countries in Southeast Asia, such as Indonesia, and behind Australia, especially its western part. East Timor does not observe daylight saving time, meaning that the time remains constant throughout the year.
- Standard Time: The standard time in East Timor is UTC +9:00 year-round. This is consistent with neighboring countries such as Japan and South Korea, though the rest of Southeast Asia follows UTC +7:00 or UTC +8:00.
Climate
East Timor has a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. The country’s climate is influenced by both its equatorial location and its rugged topography.
Coastal Region
The coastal regions, where cities such as Dili and Baucau are located, experience a tropical climate with high temperatures year-round. The temperatures typically range between 25°C and 30°C (77°F to 86°F). The climate here is influenced by the surrounding Timor Sea and monsoonal patterns, with a rainy season from December to April.
Highlands
The central highlands, where towns like Maliana and Liquiçá are located, have a slightly more temperate climate. The altitude of these areas means that temperatures are generally cooler than those in the lowland areas, with average temperatures ranging from 18°C to 25°C (64°F to 77°F).
Rainfall Patterns
East Timor experiences a wet season from November to April and a dry season from May to October. During the wet season, the country receives significant rainfall, particularly in the eastern regions. The wet season can lead to occasional flooding, especially in coastal cities. The dry season is characterized by lower humidity and more comfortable temperatures.
Economic Status
East Timor is one of the world’s youngest nations, having gained independence from Indonesia in 2002. Despite facing challenges related to post-conflict recovery, the country has made strides in developing its economy. The primary sectors that contribute to East Timor’s economy include oil and gas, agriculture, and tourism.
- Oil and Gas: The oil and gas industry is the largest sector of the economy, with revenues derived from the Greater Sunrise gas field in the Timor Sea. The country relies heavily on oil exports, and this sector contributes significantly to government revenues.
- Agriculture: Agriculture remains important to East Timor’s rural population. The country produces coffee, which is one of its main exports, alongside cocoa, rice, and cassava. The country is working on improving agricultural production and infrastructure to increase food security.
- Tourism: East Timor’s tourism industry is still in its early stages, but the country has significant potential due to its unspoiled natural beauty, beaches, and historical sites. The government is actively promoting tourism as a means of diversifying the economy.
- Challenges: East Timor faces significant challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and infrastructure deficits. The country remains heavily dependent on foreign aid and oil revenues, and there is a need for economic diversification. Additionally, the country is working to address issues related to governance, education, and healthcare.
Tourist Attractions
East Timor offers a variety of unique tourist attractions, including cultural landmarks, pristine beaches, and ecological sites. Its relatively undeveloped tourism sector makes it an attractive destination for travelers seeking to experience a more authentic and off-the-beaten-path adventure.
The Beaches of East Timor
East Timor is renowned for its beautiful, unspoiled beaches, which are ideal for activities such as diving, snorkeling, and swimming. Some of the best-known beaches include Atauro Island, which is famous for its coral reefs, and Jaco Island, a pristine, uninhabited island that is a popular destination for eco-tourists.
The Islands
Atauro Island, located just off the coast of Dili, is a popular destination for travelers seeking natural beauty, including vibrant coral reefs and secluded beaches. It is a perfect location for diving and exploring marine biodiversity.
Jaco Island is another well-known spot in East Timor, with untouched beaches and crystal-clear waters. This island is home to rich wildlife and is part of the Nino Konis Santana National Park.
Historical and Cultural Sites
East Timor’s history and struggle for independence are commemorated in several locations across the country. The Santa Cruz Cemetery in Dili marks the site of the 1991 Santa Cruz Massacre, where dozens of Timorese were killed by Indonesian soldiers. The National Museum of Timor-Leste offers visitors an in-depth look at the country’s history and culture.
Nature and Wildlife
East Timor’s natural environment is a major draw for eco-tourists. The Nino Konis Santana National Park is a protected area in the eastern part of the country, known for its biodiversity, including endemic species of birds, plants, and marine life. The park also offers excellent opportunities for hiking and trekking.
Visa Requirements for U.S. Citizens
U.S. citizens traveling to East Timor for tourism or business do not require a visa for stays of up to 90 days. However, they must possess a valid passport with at least six months’ validity from the date of entry.
For longer stays or purposes such as employment, study, or residency, U.S. citizens must apply for a visa through the nearest East Timor embassy or consulate.
Distance to New York City and Los Angeles
- Distance to New York City: The distance from Dili, the capital of East Timor, to New York City is approximately 10,000 miles (16,000 kilometers). Flights typically take between 20 to 24 hours, with layovers in major transit hubs such as Singapore or Jakarta.
- Distance to Los Angeles: The distance from Dili to Los Angeles is roughly 9,500 miles (15,300 kilometers). A typical flight takes about 18 to 22 hours, with layovers in Singapore, Jakarta, or other Asian transit points.
East Timor Facts
| Size | 14,918 km² |
| Residents | 1.38 million |
| Languages | Tetum and Portuguese |
| Capital | Dili |
| Longest river | Lóis (80 km) |
| Highest mountain | Tatamailau (2,963 m) |
| Currency | U.S. dollar |