Kenya Population
Kenya became independent from Britain’s colonial rule in 1963. After several years of economic downturn, the country’s economy has slowly but surely rebuilt, but corruption and lack of modernization still pose major obstacles to the country’s economic development. Much of the country’s population lives below the poverty line and Kenya relies on international aid.
Key figures and facts
- Capital: Nairobi
- Ethnic groups: Kikuyu 22%, luhya 14%, luo 13%, kalenjin 12%, kamba 11%, kisii 6%, meru 6%, other African tribes 15%, non-Africans (Asians, Europeans, Arabs) 1%
- Language: English (official), kiswahili (official), several origins
- Religion: Protestants 47.7%, other Christians 11.9%, Catholics 23.4%, Muslims 11.2%, traditionalists 1.7%, others 1.8, no religion 2.4% (2009)
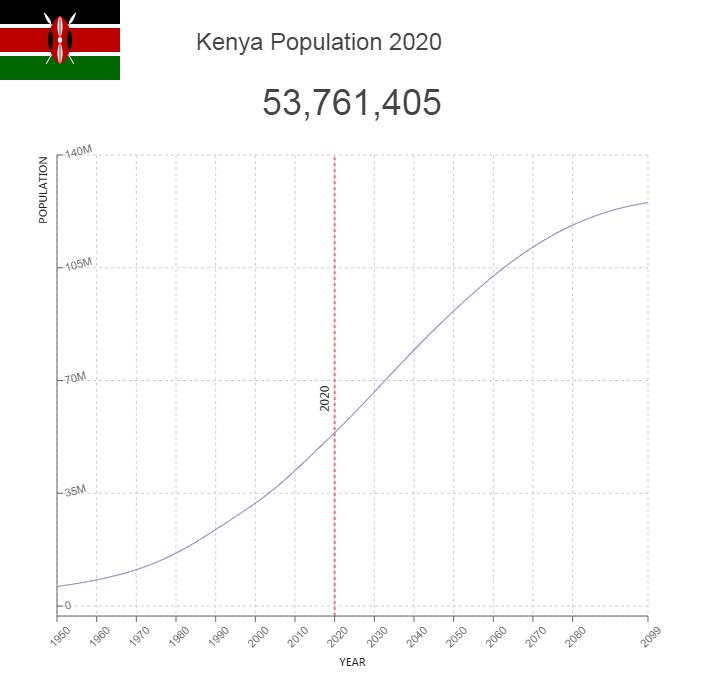
- Population: 49 700 000
- Control Form: Republic
- Area: 580 370 km2
- Currency: Kenyan Shilling
- GNP per capita: 3 155 PPP $
- National Day: December 12th
Kenya’s Population
The population of Kenya in 2020 was estimated at 53,500,000 and annual population growth to 2.2 percent. The birth rate in 2020 was calculated at 27.2 percent (against 35.5 percent in 2012, 38.5 percent in 2000 and 44.5 percent in 1990), and the death rate to 5.2 percent (against 8.5 percent in 2012, 12.3 per thousand in 2000 and 14 per thousand in 1990). The high birth rates have given the country a very young population; 39 percent are under 15 and only 3 percent are 65 or older (2020).

AIDS is a major cause of Kenya’s stagnation for a period; Among other things, child mortality increased, and the average life expectancy dropped from 57 years in 1986 to 48 years in 2005. However, in 2013, life expectancy had risen to 62.9 years for women and 59.3 years for men, and by 2020 it was up 67 years for men and 70 years for women. According to World Bank estimates, 6 percent of the adult population and around 190,000 children with HIV/AIDS lived in 2013. By 2020, that figure had dropped to 4.7 percent.
Population of Kenya by Year (Historical)
| Year | Population | Annual Growth Rate | Population Density | Global Rank |
| 2020 | 53,771,185 | 2.280% | 94.4781 | 27 |
| 2019 | 52,573,862 | 2.300% | 92.3744 | 27 |
| 2018 | 51,392,454 | 2.330% | 90.2986 | 27 |
| 2017 | 50,221,031 | 2.380% | 88.2404 | 28 |
| 2016 | 49,051,423 | 2.450% | 86.1854 | 28 |
| 2015 | 47,878,225 | 2.640% | 84.1240 | 28 |
| 2010 | 42,030,565 | 2.790% | 73.8495 | 31 |
| 2005 | 36,624,784 | 2.760% | 64.3513 | 33 |
| 2000 | 31,964,446 | 2.850% | 56.1629 | 33 |
| 1995 | 27,768,185 | 3.200% | 48.7899 | 35 |
| 1990 | 23,724,468 | 3.600% | 41.6850 | 36 |
| 1985 | 19,876,972 | 3.900% | 34.9248 | 37 |
| 1980 | 16,417,086 | 3.870% | 28.8456 | 40 |
| 1975 | 13,575,796 | 3.740% | 23.8534 | 45 |
| 1970 | 11,301,283 | 3.470% | 19.8570 | 47 |
| 1965 | 9,530,062 | 3.250% | 16.7449 | 50 |
| 1960 | 8,119,969 | 3.050% | 14.2673 | 56 |
| 1955 | 6,987,547 | 2.830% | 12.2776 | 58 |
| 1950 | 6,076,647 | 0.000% | 10.6771 | 59 |
Major Cities in Kenya by Population
| Rank | City | Population |
| 1 | Nairobi | 2,750,436 |
| 2 | Mombasa | 799,557 |
| 3 | Nakuru | 259,792 |
| 4 | Eldoret | 218,335 |
| 5 | Kisumu | 216,368 |
| 6 | Thika | 199,889 |
| 7 | Malindi | 118,154 |
| 8 | Kitale | 75,012 |
| 9 | Garissa | 67,750 |
| 10 | Kakamega | 63,315 |
| 11 | Kapenguria | 55,889 |
| 12 | Bungoma | 55,851 |
| 13 | Busia | 51,870 |
| 14 | Nyeri | 50,973 |
| 15 | Ol Kalou | 47,684 |
| 16 | Meru | 47,115 |
| 17 | Kilifi | 46,007 |
| 18 | Wajir | 45,660 |
| 19 | Mumias | 45,374 |
| 20 | Voi | 45,372 |
| 21 | Iten | 41,889 |
| 22 | Lugulu | 40,783 |
| 23 | Homa Bay | 40,208 |
| 24 | Naivasha | 38,255 |
| 25 | Nanyuki | 36,031 |
| 26 | Mandera | 35,965 |
| 27 | Narok | 35,950 |
| 28 | Kericho | 35,637 |
| 29 | Migori | 35,129 |
| 30 | Embu | 34,811 |
| 31 | Moyale | 34,203 |
| 32 | Isiolo | 33,096 |
| 33 | Nyahururu | 31,867 |
| 34 | Machakos | 31,860 |
| 35 | Rongai | 30,360 |
| 36 | Pumwani | 29,505 |
| 37 | Kisii | 28,436 |
| 38 | Molo | 27,785 |
| 39 | Kabarnet | 24,550 |
| 40 | Athi River | 24,419 |
| 41 | Lamu | 24,414 |
| 42 | Webuye | 22,396 |
| 43 | Karuri | 21,365 |
| 44 | Kiambu | 21,123 |
| 45 | Maralal | 20,730 |
| 46 | Makueni Boma | 20,570 |
| 47 | Lodwar | 20,108 |
| 48 | Kitui | 15,843 |
| 49 | Marsabit | 15,250 |
| 50 | Siaya | 15,243 |
| 51 | Kerugoya | 15,176 |
| 52 | Muhoroni | 15,106 |
| 53 | Magadi | 14,418 |
| 54 | Taveta | 13,266 |
| 55 | Kihancha | 13,051 |
| 56 | Sawa Sawa | 12,864 |
| 57 | Mariakani | 12,675 |
| 58 | Eldama Ravine | 12,413 |
| 59 | Wundanyi | 12,390 |
| 60 | Murang’a | 11,876 |
| 61 | Mwingi | 11,108 |
| 62 | Butere | 11,094 |
| 63 | Kajiado | 11,087 |
| 64 | Maua | 10,693 |
| 65 | Takaungu | 10,649 |
| 66 | Oyugis | 10,005 |
| 67 | Kangundo | 9,983 |
| 68 | Luanda | 9,942 |
| 69 | Nyamira | 9,889 |
| 70 | Ngong | 9,408 |
| 71 | Chuka | 9,236 |
| 72 | Kapsowar | 9,041 |
| 73 | Naro Moru | 8,907 |
| 74 | Ahero | 8,677 |
| 75 | Bondo | 8,572 |
| 76 | Malaba | 8,272 |
| 77 | Kinango | 7,959 |
| 78 | Baringo | 7,545 |
| 79 | Hola | 6,821 |
| 80 | Port Victoria | 6,682 |
| 81 | Limuru | 6,206 |
| 82 | Wote | 6,022 |
| 83 | Witu | 5,269 |
| 84 | Sotik Post | 5,159 |
| 85 | Gazi | 5,111 |
| 86 | Kwale | 4,772 |
| 87 | Rumuruti | 4,390 |
| 88 | Kapsabet | 3,647 |
People Groups
The majority of the population belong to various Bantu people. The largest of these groups are kikuyu, luhya and akamba, which have agriculture as a traditional main industry. The Kushite-speaking Boran and Somali and the Nilotic-speaking Masai run cattle breeding. Other large Nilotic-speaking groups are Luo and Kalenjin. Along the coast are Arabs (predominantly Mombasa) and Swahili. The Indians and Europeans, who have mainly come after 1900, are mostly in Nairobiand Mombasa. White farmers especially settled on the Kikuyu Plateau, nicknamed the White Highlands, where they reserved 33 million acres of Kenya’s best land. Most of them are now emigrated, and the land is distributed to kikuyus.
People Density
The average population density is 77.9 residents per square kilometer, but the majority is concentrated to the southwestern part of the country and to the coastal zone. About three-quarters of the population lives here on about 10 percent of the land area. The rest of the country is near the people’s land, partly because it is so water-poor. The vast majority still live in the countryside, but there is a slight influx of cities, which in 2018 had 28 percent of the population (up from 19 percent in 1989). Major cities are the capital Nairobi and the port city of Mombasa.
Religion
By 2020, approximately 83 percent of the population was Christian (48 percent Protestant, 23 percent Catholic, 12 percent were other types of Christians), while 11 percent were Muslims (mainly in coastal areas). Traditional African religions have support from around 1.2 percent. There are also Hindus, Jaina, Sikhs and followers of Bahai.
Language
Swahili (kiswahili), which is a bantu language, is the dominant interpersonal language, while English is the administrative language. Of African languages, the bantu languages are represented in the central, southeastern and western parts of the country, including kikuyu, luhya, kamba, meru, gusii. Nilotic languages are spoken in the west and northwest, including luo, kalenjin, masai, turquoise. Kushite languages are spoken in the northeast, including Somali.













































