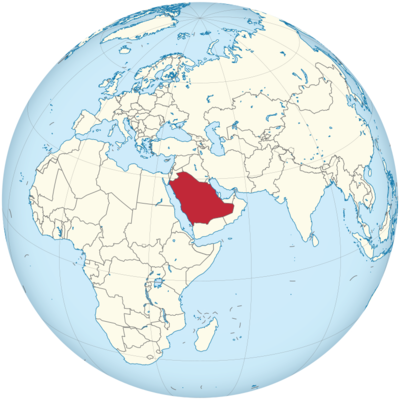
Where is Saudi Arabia Located?
Where is Saudi Arabia located on the map? Saudi Arabia is an independent nation located in Western Asia. Check out the following images to see location of Saudi Arabia on maps.
Saudi Arabia Location in World Map
Saudi Arabia is a state in the Middle East and is located on the Arabian Peninsula, covering most of the same. With a size of around 2.2 million square kilometers, the country is six times the size of Germany and four times the size of France.
Country borders
Saudi Arabia borders Jordan, Iraq and Kuwait to the north, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) to the southeast. Oman lies in the southeast and Yemen in the south. Saudi Arabia borders the Red Sea to the west and the Persian Gulf to the east. Some islands also belong to the national territory of the country.
Saudi Arabia occupies most of the Arabian Peninsula.
Mecca and Medina
Mecca is a holy city for Muslims because the Prophet Mohammed was born here. 1.4 million people live in Mecca.
Along with Mecca, Medina is one of the capitals of Islam. It is a very important city for Muslims because the Prophet Mohammed lived there. The Prophet’s tomb in the Great Mosque is also located here. Translated, Medina means “Illuminated City”. Like Mecca, Medina is closed to non-Muslims. 1.7 million people live in Medina.
Mountains
Saudi Arabia is characterized by a huge plateau with the Asir Mountains in the southwest. The highest mountain in Saudi Arabia is the Jabal Sauda with a height of 3133 meters. In the northwest there is another large mountain range called the Hejaz.
Both mountains run parallel to the Red Sea coast. The land then slopes steeply towards the Red Sea. This is followed by a 20 to 50 kilometer wide coastal plain. You can see this on the adjacent map.
Landscapes
Large parts of the country run through desert sand and scree. About 60 percent of the country is covered by the desert. In the south and south-east of Saudi Arabia there is even the largest contiguous sand desert on earth with an area of 700,000 square kilometers. This is called Rub al-Khali, which means “Empty Quarter”. It alone takes up a third of the entire country! In the northwest of the country are the red sand dunes called Nefud al-Kabir, which translates as “Great Desert”. These dunes extend over 60,000 square kilometers.
Rivers
You will hardly find any forest in Saudi Arabia, but almost 40 percent of the country is used as meadows and pastures for animals. There are no lakes in Saudi Arabia and also no “real” rivers. There are only the wadis, these are dried out river beds that fill with water during the rainy season and look like rivers for a short time because they carry water.
When the rains end, the river bed dries up again as there are no springs that could feed the river. That is why there is also a shortage of water in Saudi Arabia. But what do you do to get water? Wells are drilled to get to the groundwater and the seawater is desalinated. But neither is a perspective for the future. Wells are drying up, and seawater desalination is very expensive and uses a lot of energy.
Climate
In Saudi Arabia it is usually very hot and very dry. However, there are also very large temperature differences due to the continental climate. In summer the thermometer can easily reach over 50 degrees. In winter, temperatures can drop below freezing point. The average temperature is 28 degrees, but it usually gets much hotter in the desert landscapes.
Rain rarely falls in Saudi Arabia, and when it does, it falls between December and February. Most of the rain falls in the west of the Asir Mountains, here it can sometimes fall up to 600 millimeters, while in the rest of the country the amounts are limited to 100 millimeters.
Saudi Arabia Facts
| Size | 2,149,690 km² |
| Residents | 31.74 million |
| Language | Arabic |
| Capital | Riad |
| Longest river | – |
| Highest mountain | Jebel Sauda (3,133 meters) |
| Currency | Saudi riyal |