El Salvador Population
El Salvador means “Savior” in Spanish. The country is the smallest and most densely populated in Central America, and after a long civil war has experienced economic growth for the past two decades.
Key figures and facts
- Capital: San Salvador
- Ethnic groups: Fertilizers (descendants of Europeans + indigenous peoples) 86%, European origin 13%, indigenous people (including lenca, kakawira, nahua-Pipil) 1% (2007)
- Language: Spanish (official), Nahua and other local languages.
- Religion: Catholics 50%, Protestants 36%, Others 2%, None 12% (2014)
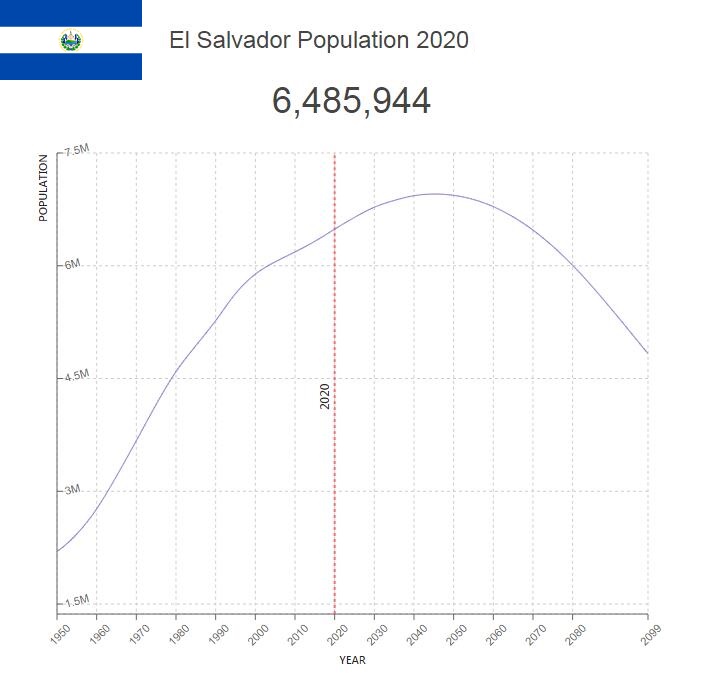
- Population: 6 378 000
- Control Form: Republic
- Area: 21 040 km²
- Currency: USD
- GNP per capita: 8 617 PPP $
- National Day: September 15th
El Salvador’s Population
El Salvador’s population is estimated at 6.2 million in 2017, based on figures from the 2007 census, and annual population growth to about 0.25 percent.

Population of El Salvador by Year (Historical)
| Year | Population | Annual Growth Rate | Population Density | Global Rank |
| 2020 | 6,486,094 | 0.510% | 313.0408 | 112 |
| 2019 | 6,453,442 | 0.510% | 311.4649 | 111 |
| 2018 | 6,420,635 | 0.510% | 309.8816 | 111 |
| 2017 | 6,388,015 | 0.500% | 308.3072 | 110 |
| 2016 | 6,356,032 | 0.490% | 306.7637 | 110 |
| 2015 | 6,325,013 | 0.450% | 305.2666 | 110 |
| 2010 | 6,183,764 | 0.430% | 298.4496 | 109 |
| 2005 | 6,052,012 | 0.550% | 292.0909 | 102 |
| 2000 | 5,887,825 | 0.910% | 284.1668 | 101 |
| 1995 | 5,628,489 | 1.320% | 271.6506 | 99 |
| 1990 | 5,269,968 | 1.320% | 254.3474 | 100 |
| 1985 | 4,936,696 | 1.460% | 238.2629 | 99 |
| 1980 | 4,591,023 | 2.020% | 221.5798 | 99 |
| 1975 | 4,154,581 | 2.490% | 200.5160 | 98 |
| 1970 | 3,672,957 | 2.790% | 177.2716 | 100 |
| 1965 | 3,201,202 | 2.960% | 154.5035 | 102 |
| 1960 | 2,766,213 | 2.600% | 133.5099 | 106 |
| 1955 | 2,432,769 | 2.030% | 117.4170 | 107 |
| 1950 | 2,199,787 | 0.000% | 106.1727 | 108 |
Major Cities in El Salvador by Population
| Rank | City | Population |
| 1 | San Salvador | 525,879 |
| 2 | Soyapango | 329,597 |
| 3 | Santa Ana | 176,550 |
| 4 | San Miguel | 161,769 |
| 5 | Mejicanos | 160,206 |
| 6 | Santa Tecla | 124,583 |
| 7 | Apopa | 112,047 |
| 8 | Delgado | 71,483 |
| 9 | Sonsonate | 59,357 |
| 10 | San Marcos | 54,504 |
| 11 | Usulutan | 51,799 |
| 12 | Cojutepeque | 48,300 |
| 13 | Cuscatancingo | 44,258 |
| 14 | San Vicente | 41,393 |
| 15 | Zacatecoluca | 39,502 |
| 16 | San Martin | 39,250 |
| 17 | Ilopango | 38,779 |
| 18 | Ahuachapan | 33,991 |
| 19 | Antiguo Cuscatlan | 33,656 |
| 20 | Chalchuapa | 32,171 |
| 21 | Quezaltepeque | 28,775 |
| 22 | La Union | 26,696 |
| 23 | Ayutuxtepeque | 25,315 |
| 24 | Acajutla | 22,652 |
| 25 | Aguilares | 21,334 |
| 26 | Sensuntepeque | 20,275 |
| 27 | Chalatenango | 19,253 |
| 28 | Izalco | 19,086 |
| 29 | Metapan | 19,032 |
| 30 | San Rafael Oriente | 18,984 |
| 31 | Puerto El Triunfo | 18,963 |
| 32 | La Libertad | 16,744 |
| 33 | San Francisco | 16,041 |
| 34 | Sonzacate | 15,335 |
| 35 | Santiago de Maria | 14,921 |
| 36 | Armenia | 14,886 |
| 37 | Santo Tomas | 14,470 |
| 38 | Santa Rosa de Lima | 13,138 |
| 39 | Zaragoza | 11,638 |
| 40 | Berlin | 11,202 |
| 41 | Guazapa | 10,884 |
| 42 | Jucuapa | 10,490 |
| 43 | Ciudad Arce | 9,984 |
| 44 | Nueva Concepcion | 9,879 |
| 45 | Juayua | 9,825 |
| 46 | Santiago Nonualco | 9,379 |
| 47 | El Transito | 9,374 |
| 48 | Atiquizaya | 9,365 |
| 49 | San Antonio del Monte | 9,024 |
| 50 | Jiquilisco | 9,018 |
| 51 | El Congo | 8,794 |
| 52 | Chinameca | 8,535 |
| 53 | Ciudad Barrios | 8,380 |
| 54 | Concepcion de Ataco | 7,686 |
| 55 | Nahuizalco | 7,247 |
| 56 | San Sebastian | 7,222 |
| 57 | San Juan Opico | 7,016 |
| 58 | Panchimalco | 6,653 |
| 59 | Nuevo Cuscatlan | 6,358 |
| 60 | Chirilagua | 6,282 |
| 61 | Olocuilta | 6,213 |
| 62 | Candelaria de La Frontera | 6,190 |
| 63 | Tonacatepeque | 6,134 |
| 64 | Santa Elena | 5,776 |
| 65 | Nueva Guadalupe | 5,687 |
| 66 | Apastepeque | 5,674 |
| 67 | Coatepeque | 5,662 |
| 68 | Suchitoto | 5,624 |
| 69 | El Rosario | 5,509 |
| 70 | Guatajiagua | 5,162 |
| 71 | Rosario de Mora | 5,067 |
| 72 | San Alejo | 5,038 |
| 73 | Tacuba | 4,944 |
Population growth
Life expectancy at birth is 78.6 years for women and 71.3 years for men (2020). Infant mortality is estimated at 16.8 per 1,000 live births in 2017, down from 33 in 2000. Around 26 percent of the population is under 15, and the infant mortality rate has dropped from around 6 in 1970 to 1.87 in 2017. Sterilization of women is the most common form of family planning.
Emigration
During the 1980s civil war, in which an estimated 77,000 people were killed, about half a million people fled to neighboring Honduras, Mexico and Nicaragua, but primarily to the United States. The emigration has continued after the war as a result of natural disasters and persistent poverty and crime. It is estimated that 20 percent of Salvadoran people live abroad today and 80 percent of them are in the United States.
Indigenous
When the Spaniards came to the country in 1524, the country was populated by a number of people divided into at least three language families (náhuatl, maya and lenca) and who lived in agricultural-based communities with varying degrees of political centralization.
The náhuatl-speaking pipilines predominated, among them especially the group cuzcatleco which has given rise to the nickname “cuzcatlecos” used about Salvadoran people in Central America. Today, the pipils are largely absorbed into the national Spanish-speaking mestizo population. In the east, lenca-speaking people dominated, in the northwest, Mayan-speaking groups such as chortí and pocomán dominated.
Today, statistics show that around 86 percent of the population are miseries, about 13 percent are white and around one percent are indigenous people. The proportion considered indigenous fell very rapidly from about 1880 when collective ownership of land was formally abolished, and especially after a pipeline uprising in Izalco in 1932. Today, however, there are trends that the number of people who consider themselves indigenous (indigenous) is rising in line with increasing recognition of collective rights. Around 1980, only 200 people spoke pipil language (nawat); in 2009 3000 people took courses in this language.
Settlement
El Salvador is the most densely populated country in Central America, with an average population density of around 313 people per square mile. The settlement is relatively evenly distributed, though with a certain overweight in the fertile valley plains that lie between the mountain ranges that cross the country longitudinally. The biggest cities are also there. In 2017, the urbanization rate was estimated at 67.6 percent. The largest cities are the capital San Salvador (about 567,000 residents in 2011; about 2.1 million in the metropolitan area), Santa Ana, Soyapango and San Miguel.
Religion
In a 2009 survey, 50.4 percent of the population said they belong to the Catholic Church, while 38.2 percent consider themselves Protestants (most of whom are Pentecostals) and 8.9 percent think they are without religion.
Language
Spanish is the official language and dominates in all social life. A few hundred speak nawat (pipil), maya spoken by immigrants from Guatemala.













































