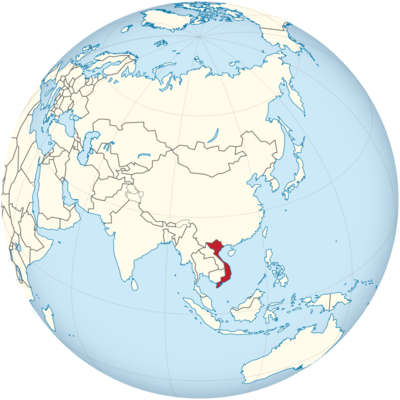
Where is Vietnam Located?
Where is Vietnam located on the map? Vietnam is an independent nation located in Southeastern Asia. Check out the following images to see location of Vietnam on maps.
Vietnam Location in World Map
Vietnam is located in Southeast Asia. Translated, Vietnam means “country in the south”. Vietnam is 331,210 square kilometers and therefore a bit smaller than Germany.
If you look at the map, the country is very elongated and covers two large climate zones: tropical climate prevails in the north and subtropical climate in the south. Vietnam stretches 1650 kilometers from north to south.
The coastline is 3400 kilometers long. Vietnam is mainly located on the South China Sea. The country borders the Gulf of Thailand only in the southwest.
There are land borders with three states. In the west, Laos and Cambodia border Vietnam, in the north lies China. In the north Vietnam extends to a maximum width of 600 kilometers, in the south of 350 kilometers. At its narrowest point, it is only 50 kilometers wide.
Like a seahorse?
If you look closely at Vietnam on the map, you will see that it is somehow shaped like an elongated “S”. It kind of looks a bit like a seahorse too, what do you think?
The shape of the country is reminiscent of an “S”.
Regions of Vietnam
Vietnam is divided into five major regions. In the south is the Mekong Delta. The Mekong River crosses a total of six Asian countries before it reaches the South China Sea in Vietnam. This region is fertile and many people live here.
To the northeast of the delta is Ho Chi Minh City, a city that was formerly known as Saigon. Although the city is no longer officially called that, the Vietnamese still call it that today. Saigon is also shorter than Ho Chi Minh City and easier to pronounce. You can also see where it is on the map above.
France in Vietnam
Many cities in Vietnam still show traces of the French today. Vietnam was part of French Indochina and part of the French colonial empire for almost 100 years. The opera house in Ho Chi Minh City was also built during the colonial era and is strongly reminiscent of French architecture. The history of Vietnam can be found in many places, reminding both visitors and locals how the country came into being.
Mountains
The Annamite Coastal Strip, a narrow coastal strip between the Annamite Mountains and the South China Sea, is very densely populated.
A little further north is the Annamite Mountains. Not that many people live here. This mountain range connects North and South Vietnam.
It follows further north the delta of the Red River, that is the region around the capital of Vietnam Hanoi. Halong Bay is also in this region and attracts tourists from near and far year after year.
In the north is the border with China. Here in the Yunnan highlands is also the highest mountain in Vietnam, which is called Phan-xi-pang and is 3144 meters high. Many ethnic minorities settle here.
Climate
If you want to travel from the north of Vietnam to the south and vice versa, you have to cross the cloud pass. This is also a weather divide for the country. A tropical climate begins in the south, while a subtropical climate predominates in the north. In the north there is a rainy season from May to September and a dry season from October to March or April. The temperatures between December and February can drop to 12 degrees. In summer the temperatures are then around 32 degrees. The rainy season lasts from June to October and temperatures are between 21 and 34 degrees.
Vietnam Facts
| Size | 331,210 km² |
| Residents | 94.51 million |
| Language | Vietnamese |
| Capital | Hanoi |
| Longest river | Red River (510 km in Vietnam) |
| Highest mountain | Phan-xi-pang (Fansipan, 3,143 m) |
| Currency | Dong |