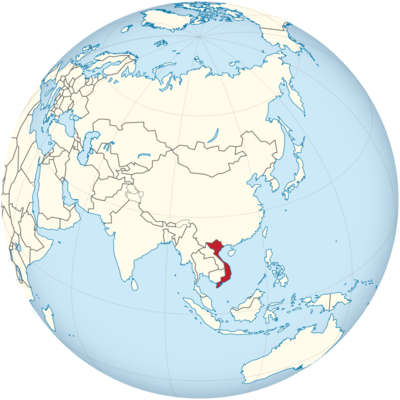
Де розташований В’єтнам?
Де розташований В’єтнам на карті? В’єтнам — незалежна держава, розташована у Південно-Східній Азії. Перегляньте наступні зображення, щоб побачити розташування В’єтнаму на карті.
Розташування В’єтнаму на карті світу
В’єтнам розташований у Південно-Східній Азії. У перекладі «В’єтнам» означає «країна на півдні». В’єтнам має площу 331 210 квадратних кілометрів, тому трохи менший за Німеччину.
Якщо подивитися на карту, країна дуже витягнута і охоплює два великі кліматичні пояси: тропічний клімат переважає на півночі, а субтропічний — на півдні. В’єтнам простягається на 1650 кілометрів з півночі на південь.
Довжина берегової лінії становить 3400 кілометрів. В’єтнам розташований переважно на Південно-Китайському морі. Країна межує з Сіамською затокою лише на південному заході.
Є сухопутні кордони з трьома державами. На заході Лаос і Камбоджа межують з В’єтнамом, на півночі — з Китаєм. На півночі В’єтнам простягається на максимальну ширину 600 кілометрів, на півдні — на 350 кілометрів. У найвужчому місці його ширина становить лише 50 кілометрів.
Як морський коник?
Якщо ви уважно подивитеся на В’єтнам на карті, то побачите, що він має форму витягнутої літери «S». Він також трохи схожий на морського коника, що ви думаєте?
Форма країни нагадує літеру «S».
Регіони В’єтнаму
В’єтнам поділений на п’ять основних регіонів. На півдні знаходиться дельта Меконгу. Річка Меконг перетинає шість азійських країн, перш ніж досягти Південнокитайського моря у В’єтнамі. Цей регіон родючий, і тут живе багато людей.
На північний схід від дельти знаходиться Хошимін, місто, яке раніше було відоме як Сайгон. Хоча офіційно місто вже так не називається, в’єтнамці досі називають його так. Сайгон також коротший за Хошимін і його легше вимовляти. Ви також можете побачити, де він знаходиться, на карті вище.
Франція у В’єтнамі
Багато міст В’єтнаму досі носять сліди французької влади. В’єтнам був частиною Французького Індокитаю та частиною Французької колоніальної імперії майже 100 років. Оперний театр у Хошиміні також був збудований у колоніальну епоху та дуже нагадує французьку архітектуру. Історію В’єтнаму можна знайти в багатьох місцях, нагадуючи як відвідувачам, так і місцевим жителям про те, як виникла країна.
Гори
Прибережна смуга Аннамітського хребта, вузька прибережна смуга між горами Аннаміт і Південнокитайським морем, дуже густонаселена.
Трохи північніше розташовані гори Аннаміт. Тут живе не так багато людей. Цей гірський хребет з’єднує Північний та Південний В’єтнам.
Далі на північ вона пролягає вздовж дельти Червоної річки, тобто регіону навколо столиці В’єтнаму Ханоя. Бухта Халонг також знаходиться в цьому регіоні та рік за роком приваблює туристів зблизька та здалеку.
In the north is the border with China. Here in the Yunnan highlands is also the highest mountain in Vietnam, which is called Phan-xi-pang and is 3144 meters high. Many ethnic minorities settle here.
Location Information of Vietnam
Vietnam is a Southeast Asian country located on the easternmost coast of the Indochinese Peninsula. The country is known for its rich culture, history, and diverse landscapes, ranging from rugged mountains and lush forests to sprawling rice paddies and long coastlines. Vietnam is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea to the east.
Latitude and Longitude
Vietnam is situated approximately between Latitude 8°N to 23°N and Longitude 102°E to 110°E. This geographical position gives Vietnam a long coastline that stretches over 3,000 kilometers (1,864 miles) along the South China Sea, making it a key player in regional maritime trade.
Capital City and Major Cities
Capital City: Hanoi
Hanoi, the capital city of Vietnam, is located in the northern part of the country. The city, which has been the political and cultural center of Vietnam for over a thousand years, is famous for its well-preserved colonial architecture, ancient temples, and vibrant street life. Hanoi is situated at Latitude 21.0285° N and Longitude 105.8542° E.
The city lies on the Red River, which has historically been an essential waterway for transportation and trade. Hanoi’s old quarter is a bustling area filled with narrow streets, traditional markets, and a blend of French and Vietnamese colonial architecture.
Major Cities
- Ho Chi Minh City (Saigon) Ho Chi Minh City, formerly known as Saigon, is the largest city in Vietnam and its economic powerhouse. Located in the southern part of the country, it is a bustling metropolis with a dynamic economy, vibrant culture, and a growing population. The city is located at Latitude 10.8231° N and Longitude 106.6297° E. Ho Chi Minh City is home to various cultural landmarks, including Notre-Dame Cathedral Basilica of Saigon, Ben Thanh Market, and the War Remnants Museum.
- Da Nang Da Nang is a coastal city located in central Vietnam, known for its beautiful beaches, historic sites, and proximity to the UNESCO World Heritage sites of Hoi An and My Son. Da Nang is a key economic hub in central Vietnam and is situated at Latitude 16.0544° N and Longitude 108.2022° E.
- Hai Phong Hai Phong is an important port city in northern Vietnam, located near the Gulf of Tonkin. The city is a major industrial center, with industries such as shipbuilding, manufacturing, and logistics. Hai Phong is located at Latitude 20.8443° N and Longitude 106.6884° E.
- Can Tho Can Tho is the largest city in the Mekong Delta in southern Vietnam. Known for its picturesque canals and floating markets, Can Tho is a key center for agriculture and trade in the region. The city is located at Latitude 10.0450° N and Longitude 105.7461° E.
- Hue Hue, located in central Vietnam, was the capital of the Nguyen dynasty from 1802 to 1945. The city is renowned for its historic imperial architecture, including the Imperial City, which is a UNESCO World Heritage site. Hue is situated at Latitude 16.4637° N and Longitude 107.5909° E.
Time Zone
Vietnam operates on Indochina Time (ICT), which is UTC +7. The country does not observe daylight saving time, so the time remains constant throughout the year.
Climate
Vietnam experiences a tropical climate, which can be classified into two major seasons: the wet season and the dry season. However, due to its varied topography, Vietnam’s climate differs from region to region.
- Northern Vietnam (Hanoi) The northern region of Vietnam experiences a distinct four-season climate, with cold winters and hot, humid summers. Winter temperatures in Hanoi can drop to 10°C (50°F), while summer temperatures can rise to 30°C to 35°C (86°F to 95°F). The wet season lasts from May to September, with the heaviest rainfall occurring in July and August.
- Central Vietnam (Da Nang, Hue) Central Vietnam has a tropical monsoon climate, with distinct wet and dry seasons. The dry season lasts from February to August, with temperatures ranging from 25°C to 35°C (77°F to 95°F). The wet season, from September to January, can bring heavy rains and occasional typhoons. Da Nang, for instance, is known for its mild winters and hot, humid summers.
- Southern Vietnam (Ho Chi Minh City, Can Tho) Southern Vietnam has a tropical climate with two distinct seasons: the wet season from May to November and the dry season from December to April. During the wet season, temperatures remain around 28°C to 32°C (82°F to 90°F), with brief but intense rainfall in the afternoons. The dry season is characterized by sunny weather and slightly cooler temperatures.
Economic Status
Vietnam is considered a developing economy with rapid growth, particularly since the country implemented economic reforms (Đổi Mới) in the late 1980s. Over the past few decades, Vietnam has emerged as one of the fastest-growing economies in Asia, driven by a combination of industrialization, export growth, and a booming manufacturing sector.
Key Sectors of the Economy:
- Manufacturing and Exports Vietnam has become a major global manufacturing hub, particularly for electronics, textiles, footwear, and furniture. It is a key exporter of products like mobile phones, garments, and seafood. In recent years, the country has attracted significant foreign direct investment (FDI), particularly from multinational companies looking to set up production facilities in Vietnam.
- Agriculture Agriculture remains an important part of Vietnam’s economy, employing a large proportion of the population. The country is one of the world’s largest producers and exporters of rice, coffee, pepper, and cashews. The Mekong Delta in the south is a key agricultural region, known for its rice production and fisheries.
- Tourism Vietnam’s tourism industry has grown rapidly in recent years, with visitors flocking to the country’s beautiful landscapes, vibrant cities, and rich cultural heritage. Major tourist destinations include Ha Long Bay, Hue, Hoi An, and the Mekong Delta. Tourism contributes significantly to the country’s GDP and job creation.
- Services and Technology The services sector, including finance, telecommunications, and information technology, has seen rapid growth. Vietnam has become a popular destination for outsourcing and IT services, thanks to its skilled workforce and competitive labor costs.
Challenges:
Despite its economic progress, Vietnam faces several challenges, including income inequality, an aging population, environmental degradation, and over-reliance on exports. However, the country is making strides toward addressing these issues through reforms and investments in infrastructure and education.
Tourist Attractions
Vietnam offers a wealth of natural beauty, historical landmarks, and cultural sites that attract millions of tourists every year.
1. Ha Long Bay
Ha Long Bay, located in northern Vietnam, is a UNESCO World Heritage site known for its dramatic limestone karsts and emerald-green waters. Visitors can take cruises, kayak through the caves, and explore the region’s islands, caves, and fishing villages.
2. Hoi An
Hoi An, a UNESCO World Heritage city, is famous for its well-preserved ancient town, traditional wooden houses, and vibrant lantern-lit streets. The city is also known for its tailor shops, where visitors can have custom-made clothing.
3. Hue
The ancient city of Hue, located along the Perfume River, was the capital of Vietnam for over a century. Its Imperial City, which includes royal palaces, temples, and gardens, is a major tourist draw. Hue also offers access to scenic sites like the Thien Mu Pagoda and the Tombs of the Emperors.
4. Phong Nha-Kẻ Bàng National Park
Цей об’єкт Всесвітньої спадщини ЮНЕСКО відомий своїми величезними печерами, зокрема Сондонг, найбільшою печерою у світі. Фонгня-кебанг – популярне місце для спелеології, трекінгу та природних екскурсій.
5. Дельта Меконгу
Дельта Меконгу, яку часто називають «Рисовою чашею» В’єтнаму, пропонує відвідувачам можливість дослідити її пишні водні шляхи, плавучі ринки та традиційні села. Туристи можуть здійснити прогулянку на човні каналами та познайомитися з місцевим способом життя.
Візові вимоги для громадян США
Громадянам США, які планують відвідати В’єтнам, потрібна віза. Найпоширеніші типи віз включають туристичні візи, ділові візи та транзитні візи. В’єтнам пропонує кілька способів отримання візи:
- Туристична віза:
Громадяни США можуть подати заявку на отримання туристичної візи через посольство або консульство В’єтнаму у своїй країні або через електронну заявку онлайн. Туристична віза зазвичай дозволяє перебування протягом 30 днів, яке в деяких випадках може бути продовжено. - Електронна віза:
В’єтнам пропонує електронну візу громадянам країн, що відповідають вимогам, включаючи США. Ця віза дозволяє перебування до 30 днів і дійсна для одноразових візитів. Заявку на електронну візу можна подати онлайн, а її схвалення зазвичай займає близько 3 робочих днів. - Віза по прибуттю:
Віза по прибуттю доступна для туристів, які прибувають літаком, але заявники повинні спочатку отримати лист-підтвердження від в’єтнамського туристичного агентства перед прибуттям до В’єтнаму. Після прибуття відвідувачі можуть забрати свою візу в аеропорту.
Відстань до Нью-Йорка та Лос-Анджелеса
- Відстань від Ханоя до Нью-Йорка
Відстань між Ханоєм, В’єтнам, та Нью-Йорком становить приблизно 12 900 кілометрів (8 000 миль). Прямий переліт зазвичай триває близько 17-18 годин, хоча більшість рейсів передбачають пересадки, що збільшує час у дорозі. - Відстань від Ханоя до Лос-Анджелеса
Відстань між Ханоєм та Лос-Анджелесом становить близько 13 200 кілометрів (8 200 миль). Тривалість польоту зазвичай становить від 18 до 20 годин, залежно від пересадок та маршрутів польоту.
Факти про В’єтнам
| Розмір | 331 210 км² |
| Мешканці | 94,51 мільйона |
| Мова | В’єтнамська |
| Капітал | Ханой |
| Найдовша річка | Червона річка (510 км у В’єтнамі) |
| Найвища гора | Фан-сі-пан (Фансіпан, 3143 м) |
| Валюта | Донг |